
All categories
Featured selections
Trade Assurance
Buyer Central
Help Center
Get the app
Become a supplier

(25230 products available)



























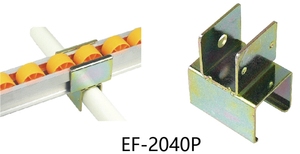

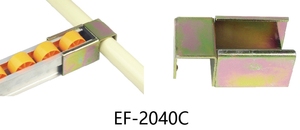






A single wheel bracket is intended for mounting one wheel, usually in light-duty applications. It is made of tough metal and is fixed to the component. That makes it easy to fix the wheel in one position while allowing rotation. These brackets are common in small carts, trailers, and light automotive systems, where stability and mobility are required but heavy weight support are required.
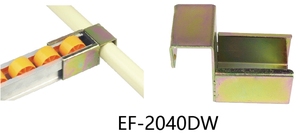
In contrast to the single wheel type, double wheel brackets have space for two wheels side by side. They give extra support because they distribute weight over a larger area. These are used in various structures, including industrial carts and warehouse racks, where the heavier load necessitates greater stability. Moreover, the double bracket provides smoother movement since the two wheels share the burden of twisting.
A swivel wheel bracket allows wheels to rotate 360 degrees. Thus, it offers precise maneuverability. Such attributes make it commonplace in applications that require flexible motion, such as shopping trolleys, caster wheels, and robotics platforms. The main advantage of this design is that it allows simple direction adjustment without changing the load's position.
As the name implies, a fixed wheel bracket restricts the wheel's movement to its rotational axis only. These are often used where straight-line travel is desired, such as in fixed-position equipment. This design is simpler and provides more stability than a swivel bracket. However, it lacks flexibility in the direction of travel.
A large counterpart to the standard wheel brackets is the heavy-duty wheel bracket. They are designed for extreme loads in demanding environments like factories, construction sites, and in vehicles meant for heavy-duty work. In addition, large materials can bear larger loads and are thus often equipped with larger wheels for easier movement over rough terrain.
The key technical specs of a wheelbarrow tire and bracket include the load-carrying capacity, degree of rotary freedom, and materials used. Notably, bearing capacity is crucial since the bracket must bear the weight of the operation meant without failing. So, a swivel or fixed wheel design should be chosen depending on whether the application requires linear travel or movement in varying directions. Lastly, materials like steel, aluminum, or reinforced polymers affect the durability and suitability of certain environmental conditions.
In addition, other optional features of the wheel bracket can be added. For instance, integrated bearings improve smoothness, a brake system for stopping the wheel's motion, or protective coatings against rust and corrosion. These can help in many ways, including heat dissipation and optimizing the system for a wider operating temperature range.
Regular maintenance of wheel brackets is needed to improve the life of the system. Mostly, it involves frequent inspections for wear, corrosion, and misalignment. Again, cleaning the area with a brush or cloth ensures no debris obstructs normal movement. Further, lubrication, using grease or oil depending on the type of bracket and wheel, should be done on a conventional basis and is recommended by the manufacturer in the manual for the product. In addition, regular checks should be made to see if all the nuts and bolts are firmly set and placed, with periodic tightening when necessary. Lastly, replacement of worn parts, such as bearings or bushings, should be done as and when required.
Indeed, large industrial carts are mostly used in warehouses and manufacturing plants. Here, the choice of the wheel bracket plays an important role in affecting the operation of the cart. For instance, heavy-duty wheel brackets provide the needed support for heavy loads and disseminate the weight evenly across all the wheels.
In the case of vehicle design and other related works, wheel brackets are used as a supporting means for securing the wheels to the axle. For example, a fixed wheel bracket is commonly found in the rear drive of a truck, while a swivel bracket is fitted on the front drive of an automobile to allow corner movements.
Single-wheel brackets, being lightweight, are used in most small trailers and tow-behind implements. In this context, there is the specific role of the wheel bracket; it ensures the bracket holds the wheel securely while allowing the wheel proper rotation for movement.
Mostly, in the commercial sector, caster wheel brackets are widely used on furniture carts for easy maneuvering around objects. Hence, the swivel wheel is particularly suited for close-quarter operations, as the wheel can turn in any direction.
Basically, in the case of mobile robots used for automation tasks, the wheel brackets have to be designed properly. Here, for instance, various types of wheel brackets are required depending on the surface and load to be transported. They also enable the robots to move in a predefined path and perform operations effectively.
The better the quality of materials that go into making a bracket, the stronger and more durable it is. While steel and aluminum are considered the most used metals due to their strength and resistance to different environmental conditions, composite materials are lightweight and offer decent strength. Thus, a more durable bracket means poor wear and tear and almost no deformation upon load.
This is crucial for any wheel bracket since overloading is a direct pathway to failure. Basically, these load ratings are defined by the application of the bracket and the type of load it usually has to bear. Overall, when a bracket is operated within its load capacity, the odds of strength and durability occurring are way higher.
Corrosion is one of the leading factors that contribute to the deterioration of wheel brackets, especially those used outdoors, in marine environments, or in countries with high humidity. As such, brackets that come with protective coatings, such as galvanization, powder coating, or stainless steel, are more durable against rusting and corrosion.
A properly designed wheel bracket distributes stress evenly across the structure. Thus, this reduces the likelihood of failure in any one area. Moreover, brackets with reinforcement support, such as gussets or thicker sections, provide added strength. This is quite crucial in high-impact or dynamic load applications.
Indeed, good maintenance practices, including regular cleaning, lubrication, and inspection, can greatly enhance the durability of a wheel bracket. In fact, maintenance eliminates debris that causes wear and tear and allows for early detection of potential issues, such as cracks or corrosion, hence giving the user time to sort them out.
A1: Actually, steel is widely used due to its high strength and resistance to deformation. On the other hand, aluminum, while not as strong as steel, is considerably lighter and is insulated against corrosion, thus making it ideal for applications in harsh environments.
A2: Basically, factors such as load capacity, the required range of motion, and the operating environment have to be considered. Hence, for heavy duty, choose a heavy-duty or a strong material repr) bracket. Meanwhile, for movements, opt for a swivel bracket. Lastly, assess the environmental condition to determine the bracket material.
A3: Moreover, the durability of wheel brackets is enhanced through regular maintenance, including inspection, cleaning, and lubrication. Also, using brackets with corrosion-resistant coatings and ensuring the loads are within capacity can improve durability.
A4: Basically, in robotics for mobile platforms, wheel brackets provide support and enable movement. Besides, different designs of brackets are actually used to achieve mobility and load-carrying capability, which is essential for the operation of robotic arms.
A5: Yes, custom wheel brackets are indeed possible. Hence, they are usually designed to turn out well for specific applications where standard brackets do not meet requirements. Therefore, advanced manufacturing techniques enable the production of these tailored wheel brackets.