
All categories
Featured selections
Trade Assurance
Buyer Central
Help Center
Get the app
Become a supplier

(1751 products available)


















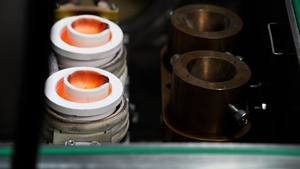









A furnace is an industrial heating device for heating and melting metal and alloys. It is the most crucial piece of equipment in any heat treatment plant. Various types of furnaces for heat treatment are developed as per the requirements of metals. Among the many methods of heating metals, the most common ones are induction heating, resistance heating, and radio-frequency heating.
Heat treatment furnaces are primarily used to strengthen and harden metal parts, such as making them impact-resistant and fatigue-proof. Such furnaces help to improve material characteristics, such as corrosion resistance, improved tensile strength, malleability, ductility, and chemical stability. They are used for the annealing, tempering, normalizing, case hardening, nitriding, and quenching of metals.
Furnaces for heat treatment are classified into categories based on their operating mechanism and design, such as:
Production capacity:
This is typically expressed in terms of the number or volume of parts that can be processed in a heat treatment furnace per unit of time. For example, an industrial heat treatment furnace may have a capacity of 1000 pieces per day.
Temperature range:
Heat treatment furnaces come in many different temperature ranges, from low to high. For example, an annealing furnace might have a temperature range of 200~800 °C, while a sintering furnace could have a higher range of 1000~1600 °C.
Heat source:
The heat source for a heat treatment furnace can be electric, gas, coal, oil, and so on. For example, an electric furnace uses electric heat as its heat source, while a gas furnace uses gas as its heat source.
Control system:
The control system of a heat treatment furnace may adopt different control modes and systems, such as PLC control, PC control, etc. For instance, a furnace may be controlled by a PLC that automatically regulates the temperature and time of the treatment.
Furnace structure:
The heat treatment furnace may have different structures, such as a top-loading, side-opening, or vertical layout. For example, a heat treatment furnace with a top-opening design provides easy access to the parts inside of it from above.
Regardless of the type of heat treatment furnace, proper maintenance is very important to ensure its stable operation and long-term use. Here are some general maintenance suggestions for heat treatment furnaces of all types:
Regular cleaning
Regularly remove the dust and dirt on the surface and inside of the heat treatment furnace so that the heat transfer surfaces can be maintained for proper heat transfer. This can prevent defects such as uneven heating and overheating.
Regular inspection
Inspect the key components of the heat treatment furnace on a regular basis, such as heating elements, temperature control devices, sealing materials, etc. Check for any signs of damage, such as wear, to ensure they are working well.
Lubrication
Appropriately lubricate the moving parts, sealing elements, etc. of the heat treatment furnace, such as bearings and sealing elements. This helps maintain smooth operation and sealing effectiveness.
Pay attention to the surrounding environment
Keep the area around the heat treatment furnace clean and tidy, and ensure that the ventilation is good. This can reduce the impact of dust and contaminants on the furnace.
The heat treatment process offers a wide array of usage scenarios in the industry. It is crucial in the metalworking industry, especially for the manufacturing of tools and metal parts.
Industrial manufacture needs:
Demand and application can be assessed by the scale, frequency, versatility, and complexity. Think about the furnace's capacity, whether it must operate continuously or intermittently, and whether it needs to process various materials or heat treatment methods.
Options for the system and controls:
Pay attention to the heating system (electrical, gas, oil, etc.), the temperature range and control accuracy, the protective atmosphere (vacuum, inert gas, etc.), and other features like automation, data logging, and integration with other equipment.
Quality assurance and compliance:
The furnace chosen must comply with industry standards and obtain the necessary certifications. Using high-quality equipment can enhance the reliability and safety of the heat treatment process.
Q1: What are some recent trends in furnaces for heat treatment?
A1: The market for heat treatment furnaces is moving toward large, centralized furnaces that can handle multiple kinds of metals and heat treatments in one place, as well as more small, self-contained units. Automation and monitoring are getting better all the time, and today even entry-level heat treatment furnaces will have computerized controls with a touchscreen interface, data logging, and networking capabilities. Furnaces are also becoming greener. Manufacturers are finding ways to cut energy use and reduce the environmental impact of heat treatment processes.
Q2: What are some common uses for heat treatment furnaces?
A2: Heat treatment furnaces are used by a wide variety of industries to strengthen and harden components. Automobile manufacturers use them to increase the strength and resilience of car parts like axles, driveshafts, gears, springs, wheels, and steering components. The oil and gas industry uses heat treatment furnaces to ensure that the critical parts of drills, pipes, valves, pumps, pressure vessels and other equipment are strong enough to carry out their vital but demanding functions, often under high pressure and risk. The aerospace industry depends on heat treatment furnaces to provide critical engine, airframe and landing gear components with the toughness they need to keep aircraft flying safely. The tool and die industry also needs heat treatment furnaces to increase the durability of the tools it makes for industries that mold and shape materials.
Q3: How does the operation of a vacuum heat treatment furnace differ from other types of heat treatment furnaces?
A3: In a vacuum heat treatment furnace, heat treatment occurs in a vacuum, preventing oxidation and contamination. This distinguishes it from atmosphere-controlled, air-firing, and other propulsion systems. Because of the high quality and purity of the results achieved with vacuum heat treatment furnaces, they are often the only affordable options for uses like aerospace engine components.
Q4: What distinguishes continuous from batch heat treatment furnaces?
A4: Batch heat treatment furnaces are typically batch processes. Materials are placed in the furnace as a whole group and as one lot. Time is then measured starting from that point. In contrast, continuous heat treatment furnaces are typically conveyor systems. Materials are steadily moved through the furnace. Continuous processes can usually run faster.