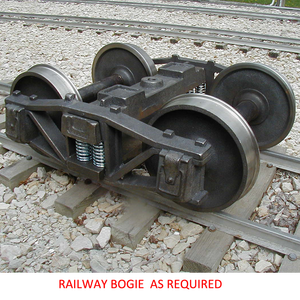
Types of Train Bogie
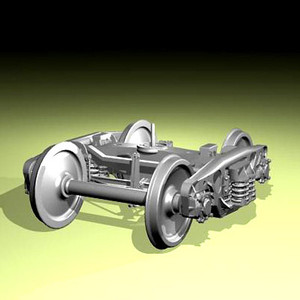
A train bogie, or a railroad bogie, is the crucial undercarriage assembly with wheels that supports the weight of the train car. Bogies play a vital role in stability, load distribution, and navigating curves and terrain variations. Let's explore the various types of general bogie in train systems:
Conventional Bogie
The most widespread type used in both freight and passenger trains, valued for its simplicity and reliability. Features two axles and four wheels connected by a sturdy frame, with leaf springs or coil springs for shock absorption and ride comfort. Ideally suited for level tracks and moderate speeds, with adaptability for various track gauges.
Best for: General-purpose applications, moderate speeds, level terrain
Bo-Bo Bogie
Also known as four-wheel bogies, these are widely implemented in light freight and passenger services. With one powered axle at each end, Bo-Bo bogies offer exceptional flexibility and tight curve negotiation capabilities. Their design makes them particularly effective for operations requiring frequent starting and stopping.
Best for: Light rail, commuter trains, operations with frequent stops
Co-Co Bogie
Features three powered axles per bogie, earning the designation of six-wheel bogie. Commonly employed in heavy freight and high-speed train applications. The Co-Co design evenly distributes weight across all six wheels, delivering superior traction and load-bearing capacity, particularly valuable for rough terrain and steep gradients.
Best for: Heavy freight, high-speed trains, challenging terrain
Three-axle Bogie
Less common than other varieties, three-axle bogies serve specialized train applications with unique requirements. Their design allows for more even weight distribution, enhanced stability, and increased load-bearing capacity. However, they tend to be more complex and costly to maintain compared to simpler designs.
Best for: Special-purpose trains, heavy loads, stability requirements
Articulated Bogie
These innovative bogies connect two train cars, enabling greater flexibility and reducing inter-car spacing. This design is particularly valuable for passenger trains where maximizing seating capacity is essential. The more complex construction of articulated bogies necessitates specialized design approaches and maintenance protocols.
Best for: Passenger trains, space efficiency, articulated train sets
Radial Bogie
Specifically designed for trains regularly navigating tight curves or routes with varying radii. Radial bogies permit lateral wheel movement, significantly reducing track and wheel wear. While offering substantial benefits for curved track operation, these bogies come with higher costs and greater complexity.
Best for: Curved routes, mountainous terrain, reducing wear
Expert Tip: When evaluating bogie types for a specific application, consider not only the current operational requirements but also future needs. Selecting a more adaptable bogie design initially may reduce the need for costly upgrades or replacements as operational demands evolve.
Comparative Weight Capacity of Bogie Types
| Bogie Type | Wheel Configuration | Best Application | Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Conventional | 2 axles, 4 wheels | General purpose | Simple, reliable, adaptable | Limited load capacity |
| Bo-Bo | 2 powered axles, 4 wheels | Light rail, commuter | Flexible, handles curves well | Less stable at high speeds |
| Co-Co | 3 powered axles, 6 wheels | Heavy freight, high-speed | Superior traction, high capacity | Complex, higher maintenance |
| Three-axle | 3 axles, 6 wheels | Special purpose trains | Even weight distribution | Expensive, complex maintenance |
| Articulated | Varies (shared between cars) | Passenger trains | Space efficient, smooth transition | Complex design, specialized needs |
| Radial | 2+ axles with lateral movement | Curved routes | Reduced wear on tracks/wheels | Expensive, mechanically complex |
Specifications and Maintenance of Train Bogies
Train bogie manufacturers provide various specifications for bogie railway systems to meet diverse operational requirements. Understanding these specifications is crucial for proper selection, operation, and maintenance.
| Specification | Description | Importance |
|---|---|---|
| Carrying Capacity | Maximum load the bogie can safely handle | Critical for safety and operational planning |
| Wheelbase | Distance between wheel centers | Affects stability and turning capabilities |
| Axle Arrangement | Number and configuration of axles | Determines load distribution and traction |
| Suspension System | Springs, shock absorbers, and linkages | Critical for ride comfort and equipment protection |
| Braking System | Type and capacity of brakes | Essential for operational safety |
| Materials | Construction materials (steel, aluminum, etc.) | Affects durability, weight, and performance |
| Traction Motor | Power and efficiency specifications | Determines acceleration and top speed |
Maintenance Requirements
Regular and thorough maintenance is essential for ensuring the safety, reliability, and longevity of train bogies. A comprehensive maintenance program should include:
Inspection Protocols
- Visual inspection of bogie frame, wheels, and components for damage or cracks
- Non-destructive testing for internal structural issues
- Measurement of wheel wear and profile
- Examination of suspension components for deterioration
Lubrication Schedule
- Bearings: Monthly application of specified lubricants
- Axles: Bi-monthly inspection and lubrication
- Suspension components: Quarterly lubrication
- Moving joints: Monthly application of appropriate greases
Brake System Maintenance
- Weekly visual inspection of brake components
- Monthly testing of brake efficiency
- Quarterly adjustment and calibration
- Bi-annual complete overhaul of brake systems
Alignment and Balance
- Monthly wheel alignment checks
- Quarterly balancing of wheels and axles
- Bi-annual track alignment verification
- Annual comprehensive geometric assessment
Warning: Neglecting regular maintenance of train bogies can lead to catastrophic failures, derailments, and significant safety hazards. Always adhere to manufacturer-recommended maintenance schedules and procedures.
How to Choose a Train Bogie
Selecting the appropriate train bogie requires careful consideration of multiple factors to ensure optimal performance, safety, and cost-effectiveness. Here's a comprehensive selection guide:
Requirements Analysis
Before selecting a bogie, thoroughly analyze the specific requirements of your rail application:
- Determine whether the bogie will serve freight or passenger operations
- Calculate required load capacity including safety margins
- Identify track gauge compatibility requirements
- Assess operational environment (climate, terrain, etc.)
Load Capacity Evaluation
Load capacity is a critical selection factor that directly impacts safety and performance:
- Calculate maximum expected load including cargo, passengers, and equipment
- Apply a safety factor of at least 20% above maximum load
- Consider dynamic loading conditions during acceleration and braking
- Evaluate uneven load distribution scenarios
Track Compatibility
Ensure the bogie is fully compatible with the rail infrastructure:
- Verify track gauge measurements match bogie specifications
- Evaluate minimum curve radius capabilities against route requirements
- Consider track quality and maintenance standards
- Assess compatibility with switches, crossings, and other track features
Maintainability Assessment
Factor in long-term maintenance considerations:
- Evaluate accessibility of components for inspection and maintenance
- Consider availability of spare parts and service support
- Assess maintenance interval requirements
- Calculate total lifecycle maintenance costs
Selection Tip: When choosing between bogie options, consider developing a weighted decision matrix that accounts for all relevant factors including cost, performance, maintenance requirements, and compatibility with existing systems. This approach helps ensure an objective selection process that aligns with your specific operational needs.
| Selection Factor | Considerations | Importance Level |
|---|---|---|
| Axle Load Distribution | Even distribution prevents track damage and ensures stability | Critical for freight applications |
| Suspension System | Affects ride quality, stability, and component lifespan | Essential for passenger comfort |
| Weight and Size | Impacts train efficiency and operational limitations | Important for energy efficiency |
| Environmental Adaptability | Ability to operate in various climates and conditions | Critical for certain routes |
| Manufacturer Reputation | Track record for quality, reliability, and support | Significant for long-term reliability |
| Lifecycle Costs | Initial purchase plus ongoing maintenance expenses | Critical for financial planning |
DIY Train Bogie Replacement Guide
While bogie replacement is typically performed by trained professionals, under certain circumstances, knowledgeable individuals may undertake this task with proper precautions. This guide outlines the essential steps for safely replacing a train bogie:
Safety Warning: Bogie replacement involves working with heavy components and potentially hazardous systems. This procedure should only be attempted by individuals with appropriate technical knowledge, skills, and safety equipment. Always consult official service documentation for your specific train model before proceeding.
-
Ensure Safety First
Before beginning any work, implement comprehensive safety measures:
- Position the train on level, stable ground with adequate workspace
- Apply all parking brakes and use wheel chocks to prevent movement
- Disconnect all power sources and verify power isolation
- Don appropriate personal protective equipment (safety glasses, gloves, steel-toed boots)
- Ensure proper lighting and ventilation in the work area
-
Diagnose the Problem
Before full replacement, determine if repairs might suffice:
- Remove access panels to fully inspect the bogie assembly
- Check for worn wheels, damaged bearings, or cracked components
- Inspect for loose fasteners or broken suspension elements
- Document all findings to inform replacement decisions
-
Prepare for Removal
Setup and preparation are critical for safe bogie removal:
- Position appropriate lifting equipment (jacks, stands, or hoists)
- Disconnect electrical connections, clearly labeling each one
- Remove brake linkages and pneumatic connections
- Support the train car body securely before releasing the bogie
-
Remove the Old Bogie
Carefully extract the damaged bogie using proper techniques:
- Loosen and remove all mounting bolts and retaining hardware
- Gradually lower the bogie using controlled movements
- Use appropriate equipment to safely move the heavy bogie away
- Inspect the mounting points on the car body for damage
-
Install the New Bogie
Properly position and secure the replacement bogie:
- Carefully position the new bogie under the train car
- Raise into position ensuring proper alignment with mounting points
- Install all mounting hardware to manufacturer specifications
- Reconnect all electrical, pneumatic, and mechanical connections
-
Test the Installation
Verify proper function before returning to service:
- Perform a comprehensive visual inspection of all connections
- Test electrical systems for proper operation
- Verify brake system functionality
- Conduct a controlled test run to confirm proper operation
Maintenance Tip: When replacing a bogie, take the opportunity to thoroughly clean and inspect all interface points between the bogie and car body. Address any corrosion, wear, or damage to prevent future issues. Also, consider upgrading wear components if newer, more durable alternatives are available for your train model.
Frequently Asked Questions
A bogie is a specialized chassis or frame that houses the wheels, axles, and suspension for a rail vehicle, supporting the train car body above it. In contrast, a car is a personal automobile designed for road travel with an integrated body and chassis designed to carry a few people. The fundamental difference lies in their application (rail vs. road) and their structural relationship to the vehicle they support.
Yes, bogie-like systems can be adapted for use in automotive applications, particularly in high-performance cars where improved stability and handling are priorities. These automotive "bogies" typically take the form of sophisticated independent suspension systems that borrow principles from rail bogie design. They help distribute weight more effectively, improve cornering, and enhance overall vehicle dynamics. However, these systems differ significantly from true rail bogies in their design, as they must accommodate steering, variable speeds, and road conditions rather than fixed rail guidance.
The most critical components of a train bogie include:
- Wheels and Axles: Form the fundamental interface with the track, supporting the entire weight of the train while providing guidance along the rails
- Suspension System: Consists of primary suspension (between wheels and bogie frame) and secondary suspension (between bogie and car body), absorbing vibrations and impacts
- Bogie Frame: The structural backbone that integrates all components and transfers loads between the train car and the wheels
- Bearings: Allow smooth wheel rotation while supporting immense loads
- Braking System: Provides crucial stopping power through various mechanisms (disc, tread, or regenerative)
These components work in concert to support the train's weight, enable smooth movement along tracks, absorb vibrations and impacts, and provide safe deceleration when needed.
Train bogies require regular inspection on a tiered schedule:
- Daily Visual Checks: Basic examination for obvious damage or issues
- Weekly Inspections: More detailed examination of key components like wheels, brakes, and visible suspension elements
- Monthly Comprehensive Inspections: Detailed assessment of all bogie components including bearings, suspension, and frame integrity
- Annual Overhauls: Complete disassembly, thorough inspection, and component replacement as needed
This schedule may vary based on operational intensity, environmental conditions, and regulatory requirements. High-speed and passenger services typically require more frequent inspections than freight operations.

















































































































































































































































 浙公网安备 33010002000092号
浙公网安备 33010002000092号 浙B2-20120091-4
浙B2-20120091-4