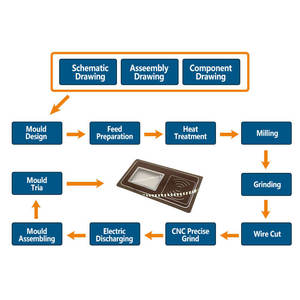
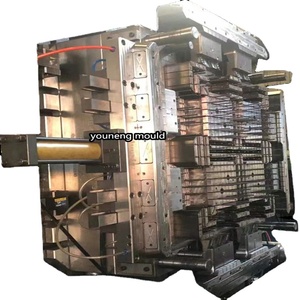
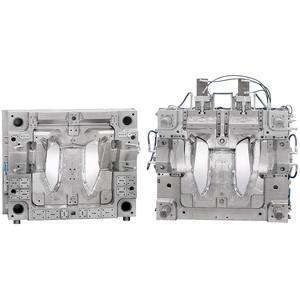
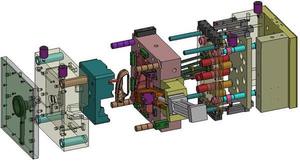
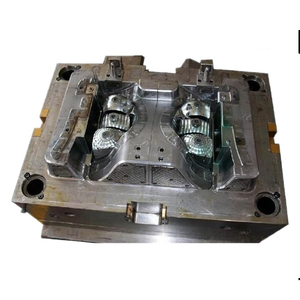
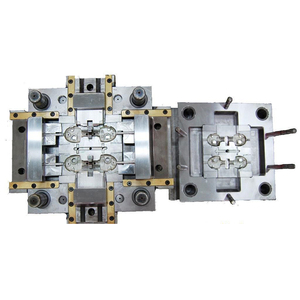
Introduction to Reverse Injection Mold
The reverse injection mold is a revolutionary advancement in the realm of plastic manufacturing, catering to industries seeking enhanced precision and efficiency. This innovative molding technique is designed to create intricate shapes that meet the unique requirements of a variety of applications. Reverse injection molding eliminates many of the drawbacks associated with traditional molding, paving the way for higher productivity, lower waste, and more consistent product quality.
Types of Reverse Injection Molds
Understanding the various types of reverse injection molds can help businesses select the most appropriate solution for their needs. The main types include:
- Cold Runner System: Utilizes a cold channel for delivering molten plastic, reducing cycle times and material wastage.
- Hot Runner System: Employs a heated channel to keep the plastic molten during the molding process, enhancing overall efficiency.
- Multi-cavity Molds: Designed to produce several parts in a single cycle, maximizing productivity for high-volume production.
- Stack Molds: Allows for multiple layers of parts to be produced simultaneously, ensuring increased output and design flexibility.
Applications of Reverse Injection Mold
Reverse injection molds find a diverse range of applications across various sectors, thanks to their flexibility and precision. Notable applications include:
- Automotive Industry: Used for creating complex components such as dashboards, switches, and other critical parts.
- Consumer Electronics: Ideal for manufacturing intricate housings and electronic fixtures.
- Medical Devices: Employed in producing components requiring tight tolerances and biocompatibility.
- Aerospace: Suited for lightweight and durable parts that meet stringent regulatory standards.
Advantages of Reverse Injection Mold
The benefits of utilizing reverse injection molds are numerous, making them an excellent choice for manufacturers looking to optimize their production. Key advantages include:
- Enhanced Precision: Achieves tighter tolerances in production, allowing for more complex designs and intricate parts.
- Improved Material Utilization: Significantly reduces waste by recycling excess plastic, contributing to a more sustainable manufacturing process.
- Faster Production Cycles: Minimizes downtime with quicker injection and cooling processes, leading to a more streamlined workflow.
- Design Flexibility: Supports a wide array of materials and blends, accommodating custom formulation and design requirements.