
All categories
Featured selections
Trade Assurance
Buyer Central
Help Center
Get the app
Become a supplier

(20148 products available)





































Pneumatic piston pumps are often classified according to their structural and operational characteristics. The main types include the following:
Single-acting pneumatic piston pump
Single-acting pneumatic piston pumps use air pressure on one side of the piston to pump fluid through one stroke. This makes them effective for low-viscosity liquids. The type is further classified into the following sub-types:
Single-acting diaphragm pump: This pump uses a diaphragm instead of a piston to pump liquids. It is ideal for handling corrosive or hazardous fluids due to its ability to isolate the pumped fluid from the mechanical parts.
Single-acting piston pump: This type is used for higher pressure applications. Moreover, these pumps are generally simpler in construction and can handle a wider range of viscosities compared to diaphragm pumps.
Double-acting pneumatic piston pump
Double-acting pneumatic piston pumps use air pressure on both sides of the piston to pump fluid on both strokes. This makes them more effective than single-acting pumps, which pump fluid on only one stroke. They also produce a more constant and higher flow rate. The type is further classified into the following sub-types:
Double-acting diaphragm pump: Just like the single-acting diaphragm pump, this type also uses a diaphragm to pump fluid. It can handle both low and high-pressure applications that require the movement of larger volumes of fluids.
Double-acting piston pump: This type uses a piston to pump fluid which can be used in high-pressure applications as well as for a wide range of fluid viscosities.
Rotary pneumatic piston pump
This type of pump uses a rotating mechanism instead of a linear piston to pump fluid. Its mechanism is particularly suited for continuous operation, making it ideal for high-viscosity fluids. This pump type is less pulsating compared to reciprocating pumps.
Manufacturing industry
Pneumatic piston pumps are used in the manufacturing industry to move and dispense lubricants in machinery parts during operation. The pumps then boost operational efficiency by ensuring parts with moving elements are optimized.
They Move hydraulic fluids used in the operation of hydraulic-powered machinery like hydraulic presses and benders. The pneumatic piston pumps provide high-pressure fluid transfer required for effective hydraulic system operation.
Pneumatic piston pumps also dispense chemicals like solvents, acids, and other fluids used or generated in the manufacturing processes. These pumps then ensure precise and safe chemical movement that boosts process efficiency and worker safety.
Construction industry
Pneumatic piston pumps are used to transport materials like concrete, mortar, and other slurries used in the construction processes. The pumps then offer high pressure and efficiency, allowing them to move heavy and thick materials vertically and horizontally across construction sites.
Mining industry
Pneumatic piston pumps are utilized in the mining industry to move slurry, a mixture of water and mineral particles used to mine minerals and transport them to other places. The pumps' high efficiency and ability to handle abrasive materials make them ideal for this application. The pumps are also used to transfer chemicals that are necessary in mineral processing.
Oil and gas industry
Pneumatic piston pumps are used in the oil and gas industry to transport drilling mud, a mixture of water and other chemicals used during drilling for mineral and fossil fuel. The pumps' ability to handle high viscosity and pressure is ideal for this application. The pumps are also used to move and dispense various lubricants used in machinery maintenance and part repair.
Agriculture industry
Pneumatic piston pumps are used in the agriculture industry to spray pesticides and herbicides on crops. They ensure the conversion of chemicals into fine mist, which is evenly distributed across the target area for effective crop treatment.
Chemical industry
Pneumatic piston pumps are used in the chemical industry for diverse fluid movements such as the transfer of corrosive chemicals, viscous substances, and toxic materials. They ensure safe and efficient movement due to their ability to handle high pressures and various fluid viscosities.
Pharmaceutical industry
Pneumatic piston pumps are used in the pharmaceutical industry for processes like fluid transfer, mixing, and dispensing. They ensure precise movements required for process accuracy, which impacts the quality of pharmaceutical products.
Maintaining pumps in diverse industries
In diverse industries, pneumatic piston pumps are used for pump maintenance. They move lubricants and other fluids used to clean, repair, and maintain different types of pumps, ensuring their longevity and optimal performance.
High efficiency and performance
Pneumatic piston pumps are highly efficient in transferring high volumes of fluids quickly. They produce great pressure, increasing their capability to pump fluids to great heights or long distances. They also operate continuously without overheating, which makes them ideal for heavy-duty applications.
Versatility
Pneumatic piston pumps are used in various industries like manufacturing, construction, and mining, to move diverse fluids ranging from water to industrial chemicals. Moreover, they can handle low to high viscosity, which makes them suitable for many diverse applications.
Safety and reliability
Pneumatic piston pumps use compressed air as their power source, which makes them ideal for use in environments with explosive or flammable liquids as they do not generate electric sparks. They are also highly reliable and operate in rugged conditions with minimal maintenance.
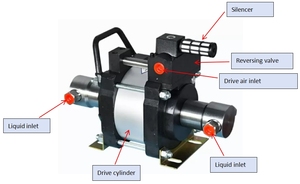
Pulsation dampeners
Some pneumatic piston pumps are fitted with pulsation dampeners. These devices smooth the fluid flow, reducing the pressure variations that cause pulsation.
Corrosion-resistant materials
To handle abrasive fluids, many pneumatic piston pumps are manufactured with corrosion-resistant materials like stainless steel, aluminum, or specialized polymers.
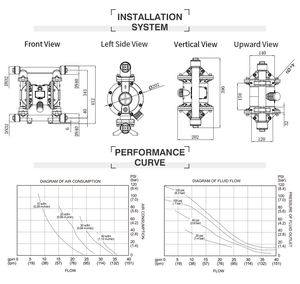
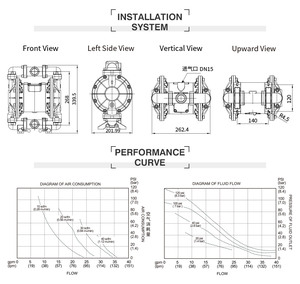
Air consumption
These pumps are designed with efficiency in mind, hence consuming minimal amounts of air while maximizing their output.
Operating pressure
This is usually between 30 to 120 psi for most applications; however, certain heavy-duty models may go up to 1.000 psi.
Flow rate
The flow rate generally ranges from 0.1 to 80 gallons per minute, depending on the model and application.
Fluid viscosity
These pumps generally handle fluids with viscosity ranging from 0 to 1.000 centipoise. However, certain models can handle up to 50.000 centipoise for high-viscosity applications.
Materials
Pneumatic piston pumps are commonly constructed from materials like aluminum, stainless steel, and plastic. Which one is used depends on the pump’s model, intended application, and the type of fluid being moved.
Seal materials
To ensure compatibility with various fluids, seals in pneumatic piston pumps are manufactured with materials like nitrile, polyurethane, and fluorocarbon.
Ball materials
The balls in the check valve are manufactured with diverse materials like ceramic, stainless steel, and tungsten carbide. They can be selected based on compatibility with the pumped fluid or required resistance to wear.
Diaphragm materials
Pneumatic piston pump diaphragms are manufactured with materials like rubber, teflon, and neoprene. Like the seals, these materials can be adapted to ensure compatibility with the fluids.
Significant factors
Several factors need consideration to choose the right pneumatic piston pump for a particular business client. These factors include the fluid’s nature, a pump’s desired pressure and flow rate, and space constraints.
Fluid compatibility
When choosing pneumatic piston pumps, it is vital to ensure that a pump’s materials of construction are compatible with the fluid a client will move. This is crucial because any incompatibility will lead to corrosion, damage, or contamination. It is necessary to consider the fluid’s viscosity, temperature, and chemical composition to select appropriate materials such as elastomers and metals.
Pressure and flow rate
A pump's pressure and flow rate should match the application requirements. A pump with a higher flow rate provides quicker fluid movement, while one with greater pressure offers resistance to back pressure and system choke points. Thus, considering these parameters ensures that the chosen pump performs effectively without incurring overloads and overheating.
Maintenance requirements
Some pumps are preferred over others because of their minimal maintenance needs, which afford greater uptime. Pneumatic piston pumps with fewer parts and easy access for maintenance should be prioritized.
Noise levels
The pumps usually operate with high noise levels, especially if they are in a section where personnel work. In such an environment, it would be ideal to use options with noise-reduction features or silencers to mitigate their high noise levels.
Space constraints
If there are space limitations, it would be ideal to use compact pneumatic piston pumps that easily fit the available space. However, this should not come at the expense of the required performance capabilities.
Efficiency
Pneumatic piston pumps are very efficient in moving liquids, especially in high-volume and high-pressure situations. They offer great power-to-speed ratios that enable them to handle heavy workloads effectively. Moreover, they maintain their efficiency even in harsh environments where other types of pumps fail to perform.
Versatility
The pumps can handle a broad spectrum of fluid viscosities, including slurries, chemicals, and water. This makes them suitable for many industries, ranging from manufacturing to construction. They also can operate in challenging conditions, including extreme temperatures and hostile environments like those containing explosive or corrosive chemicals.
Reliability and durability
Pneumatic piston pumps are designed to be robust and durable in harsh environments, including dust, extreme temperatures, and high humidity. This is why they are preferred for outdoor applications. Furthermore, they require minimal maintenance. This is because many components are internally lubricated, which reduces wear and tear.
Safety
The pumps are powered by compressed air, which makes them ideal for using flammable and hazardous fluids in environments where electrical equipment poses sparks. They also come with various safety features like pressure relief valves and exhaust silences to prevent noise and pressure shocks.
Noise pollution
Pneumatic piston pumps operate at high noise levels after they have been in use for some time. This can make the environment uncomfortable for personnel working around them. Continuous exposure to such deafening noise levels leads to hearing damage.
Cost of compressed air
Pneumatic piston pumps are powered by air. Although this air is not very expensive to generate, its cost will increase over time, especially if the pump has to run constantly. Thus, the operational overhead can become significant in the long term, especially for high-duty applications.
Energy efficiency
Although they are efficient at moving liquids, pneumatic piston pumps are not always the most energy-efficient option available. It takes more energy to produce compressed air mechanisms that power the air-driven motors than using electric motors.
Complexity
The pumps usually have complicated control systems. They also require specific air pressure and flow rates for optimal functioning. Meeting these requirements necessitates additional systems like air compressors and regulators, which eventually complicate the operations.
The main difference between the two is their power source and the environments they operate in. A pneumatic piston pump is powered by compressed air and is usually deployed in environments that demand low to moderate pressure. On the other hand, hydraulic piston pumps use liquids, which are typically high-pressure applications. They are usually found in environments that cannot contain gases.
Yes, certain pneumatic piston pumps are ideal for high-viscosity fluids. However, diaphragm and double-acting piston pumps are better suited for these fluids. High-viscosity fluids are thicker fluids like oils, slurries, and pastes.
Some pneumatic piston pumps handle corrosive fluids, especially those constructed with chemical-resistant materials like teflon, stainless steel, or specialized polymers. Customers have to specifically request such pumps.
Although they are one of the lowest-maintenance pumps, pneumatic piston pumps still require some maintenance. For example, regularly checking and replacing worn-out seals and diaphragm is a must. Moreover, lubricating internal components is sometimes necessary. Since they operate for longer periods, they require more frequent checks and maintenance. This is because they tend to accumulate more dust and debris than other models.
Some common safety features include pressure relief valves that prevent overpressure situations, exhaust silencers that minimize noise, and regulatory controls to prevent operating a pump beyond its limitations.