(2276 products available)






















































































































































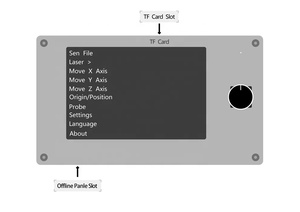




































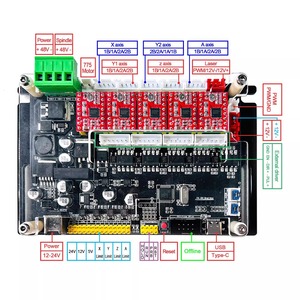














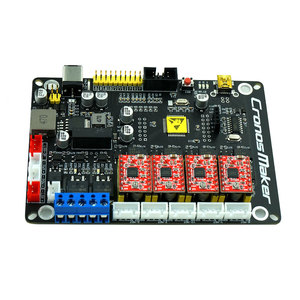



An Offline CNC controller allows users to control a CNC machine without a computer directly. These devices are provided with several features and functionalities to enhance the overall CNC machining experience. The types of offline CNC controllers can be classified according to their design, functionality, operation, application, and compatibility.
The specifications for an offline CNC controller may vary based on the particular model and manufacturer. However, some general specifications are as follows:
As the offline CNC controller manages the operation of the entire CNC machine, it is essential for both the function of individual machines and the quality of the processed materials to maintain the controller. During use, the controller and its surroundings should be kept dry and well-ventilated in order to avoid overheating. The controller should be prevented from being exposed to sunlight or rain. Water and dust should also be kept at a distance from the controller. The screen and other parts of the controller should be gently wiped and cleaned with a soft towel to avoid any scratches or damage to the device. In daily use, offline CNC controllers are usually used to set up and control the processing of materials on the CNC machine. It is necessary to avoid frequent plugging and unplugging of the connection lines so as to reduce the wear and impact on the controller. Also, the firmware of the offline CNC controller should be updated from time to time according to the manufacturer's instructions. This helps to improve the performance and stability of the controller, as well as to add new features and functionality.
Due to their flexibility, ease of use, and low maintenance requirements, offline CNC controllers are employed in various applications across numerous industries.
Small-scale workshops and fabricators
Offline CNC controllers are commonly used in small-scale workshops and fabricators that cannot afford large-scale online CNC control systems. These offline controllers provide an economical solution for fabricators to automate their cutting, engraving, and milling operations without requiring complex networking capabilities.
Metal and wood processing industries
Offline CNC controllers find widespread use in metal and wood processing industries. Whether dealing with metal materials like steel, aluminum, or copper, or working with various types of wood, offline CNC controllers enable precise cutting, engraving, shaping, and detailing tasks. These controllers enhance productivity, improve product quality, and streamline processing workflows in both metal and wood industries.
Teaching and training purposes
Offline CNC controllers are employed for teaching and training purposes in technical schools, vocational institutes, and engineering colleges. These controllers provide an affordable yet effective solution for educational institutions to train students in CNC technology, machining techniques, and programming skills. By using offline CNC controllers, students can gain hands-on experience, learn to design and execute CNC programs, and develop practical CNC machining proficiency.
Prototyping and product development
In the realms of prototyping and product development, offline CNC controllers prove to be invaluable tools. Whether in electronics, automotive, or other industries, these controllers enable engineers and designers to swiftly manufacture prototypes and test models. With offline CNC controllers, the process of product development is accelerated, iterations are facilitated, and the time to market for new products is reduced.
Repair and maintenance services
When it comes to repair and maintenance services, offline CNC controllers are employed to facilitate the repair of CNC-machined components and equipment. These controllers assist technicians in ensuring precise repairs and maintaining the quality of CNC machining. Additionally, offline CNC controllers are useful for mobile repair services, enabling machining repairs on-site or in remote locations.
When choosing an offline CNC controller, focus on the features, compatibility, ease of use, and application requirements.
Controlling functions
Select a controller that can perform the functions customers want to use. For example, the controller can perform tasks like controlling feed rate, spindle speed, tool selection, and operation direction. Some of them can even control more complicated things, such as determining the shape of a workpiece and the position of a cutter through advanced mathematical calculations. It's also important to check if the selected device can be programmed to suit a specific task better.
Controller and machine compatibility
Ensure that the offline CNC machine controller is compatible with the existing CNC machines. Both devices should work together without unnecessary adjustments or complicated installation processes. A typical case of incompatibility is the failure of a new controller to connect with the existing motor and driver.
User-friendliness
Understand the users who will work with the CNC controller and select a device at the right level of complexity for them. Controlling parameters should be clear, logically organized, and intuitive. Manuals, helpful documentation, and customer support should also be considered.
Application-specific requirements
The above factors are particularly important in selecting an offline CNC router controller. For a router, things like material types, desired cutting techniques, and the complexity of the workpieces to be processed should be taken into account when determining which features and functions are essential.
Q1: What does an offline CNC controller do?
A1: An offline CNC controller may be used to directly control a CNC machine without the necessity for a computer connection or to prepare files for a CNC machine. It enables the user to program the machine manually, edit the configurations, and carry out diagnostics and maintenance tasks without the need for a computer.
Q2: Is an offline CNC controller the same as a pendant?
A2: No. While both are used to control CNC machines, the offline controller is used to program the machine, while a CNC controller pendant provides manual control over the movement of the machine. The pendant usually acts as a supplementary device to the CNC controller.
Q3: Can I connect an offline CNC controller to any CNC machine?
A3: Not necessarily. CNC controllers come in different types and models that are suitable for specific machines like routers, mills, plasma cutters, and others. One must carefully consider the compatibility between the offline CNC controller and the CNC machine at hand to ensure proper functioning.
Q4: What features does an offline CNC controller have?
A4: Offline CNC controllers can have many features depending on the specific type and model. Typical features may include a large LCD screen to show the user interface and machining details, a programmable function for custom machining configurations, a file storage capacity to hold machining files, and a USB connectivity function for file transfer, among other things.
Q5: Can I upgrade my CNC machine's controller?
A5: Yes, it is possible to replace the existing controller with a new one as long as it is of the same type and is compatible with the machine. Business buyers should consult a qualified technician before proceeding with the upgrade to make sure it is safe and possible.