
All categories
Featured selections
Trade Assurance
Buyer Central
Help Center
Get the app
Become a supplier

(7240 products available)


































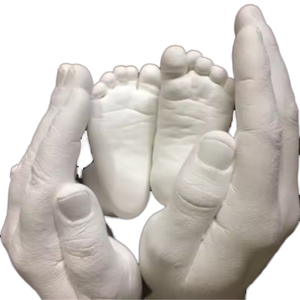





3D plaster mold is a type of mold used to create three-dimensional shapes and designs with plaster. These molds are typically made from durable materials like silicone, polyurethane, or plaster itself. They can reproduce intricate details and deep textures, such as floral patterns, geometric shapes, or custom designs. 3D plaster molds are commonly used in art, architecture, and interior design to create decorative elements, castings for walls, or architectural features. Plaster poured into these molds takes the shape of the mold, resulting in a 3D replica of the mold's design once the plaster hardens and the mold is removed.
Using a 3D plaster mold has many advantages. First, it enables the mass production of complex designs, making them more affordable for decorative elements and architectural features. It also allows for customization, as molds can be made to fit specific design requirements. Additionally, plaster is a cost-effective and easy-to-work material, and molds provide a smooth surface and fine detail reproduction. They are used in many sectors, including building, film, and theater, where realistic props and set designs are needed. With advancements in 3D printing, creating molds for plaster casting has become more accessible and cost-effective.
There are several types of 3D plaster molds, each with unique features and advantages. Depending on the application, these types range from flexible silicone molds to rigid plaster-of-paris molds.
3D Design Creation:
The process begins with a 3D design of the desired object. This is usually done using Computer-Aided Design (CAD) software. The design can be anything from a simple geometric shape to a complex artistic relief. The software allows for precise control over the dimensions and details of the object.
Material Selection:
Molds for 3D plaster are made from various materials, each with its advantages and disadvantages. Common materials include silicone, latex, and urethane rubbers. These materials are flexible and can capture fine details of the design. They are also durable, which means the mold can be used multiple times. Some molds may use rigid materials like plaster or fiberglass for added support or when needed to reproduce flexible moldings.
Mold Making Process:
The mold-making process involves several steps. First, the 3D design is printed or projected onto a physical model to ensure accuracy. Then, the chosen mold material is mixed and poured over the model into a mold box. After it cures and hardens, it is carefully removed from the model. Any excess material is trimmed, and the mold is cleaned and prepared for use.
Casting the Plaster:
Once the mold is ready, plaster casting can begin. Plaster powder and water are mixed to form a slurry in a bowl. The mold is cleaned and lightly coated with a release agent to prevent the plaster from sticking to the mold. The plaster slurry is poured into the mold, making sure to fill all cavities. For larger or more complex pieces, the plaster can be poured in two or more sections. The mold is tapped gently to remove air bubbles and ensure the plaster fills all details. The filled mold is left to set for several hours until the plaster hardens.
Mold Cleaning and Maintenance:
After casting, the mold must be cleaned to remove any plaster residue. This is usually done with warm water and a soft brush. If the mold material is sensitive, specialized cleaners may be used. Proper cleaning extends the mold's life and ensures it works well for future casts.
3D plaster molds are used in different fields. They create three-dimensional shapes and intricate designs. Here are some key applications of 3D plaster molds:
Plaster molds have a high level of durability. They can withstand the wear and tear of the casting process. So, they are ideal for industries that need heavy use of molds. For example, the jewelry industry uses plaster molds to make rings and necklaces. In the glass industry, plaster molds are used to make glass products. They are also used in the cement industry to make cement products.
Choosing a 3D plaster mold is an important step in creating 3D plaster moldings. Different kinds of molds can be used to make different kinds of designs. When choosing a mold, these things should be considered:
These factors should be considered when choosing a 3D plaster mold. Considering these factors will help to choose a mold that fits the needs and works well. Choosing the right mold is key to making great 3D plaster designs.
Q1: What are the benefits of 3D plaster molds compared to traditional molding techniques?
A1: 3D plaster molds offer enhanced design flexibility, precise reproduction of intricate details, and faster production times. They enable the creation of complex geometries and custom shapes that may be challenging to achieve with traditional molding techniques.
Q2: What types of plaster can be used with 3D molds?
A2: Various kinds of plaster can work well with 3D molds, including casting plaster, gypsum plaster, and lightweight or high-strength plasters. The choice depends on factors like the desired finish, strength requirements, and curing time.
Q3: How can one ensure a good release of the cast from the mold?
A3: Applying a mold release agent such as silicone spray or wax to the 3D mold before pouring in the plaster helps ensure a smooth release of the cast. It prevents the plaster from sticking to the mold and protects the mold for repeated use.
Q4: What is the process of using a 3D plaster mold?
A4: Using a 3D plaster mold involves mixing the plaster according to the manufacturer's instructions, pouring it into the mold, and then allowing it to cure. The specific steps may vary depending on the type of mold and plaster used but generally include preparation, pouring, and curing stages.
Q5: How can one care for and maintain a plaster cast made from a 3D mold?
A5: A plaster cast should be handled with care to maintain it, as it is fragile and can be chipped or cracked. It should also be kept away from water or high humidity, as this can weaken the plaster. If a protective finish is required, sealing the cast with a suitable sealant can help protect it from moisture and dust.