(3337 products available)





























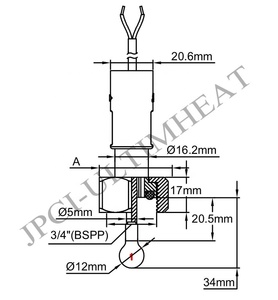













































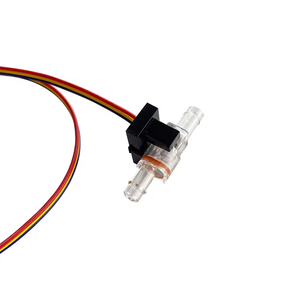
















































































































Micro flow sensors come in various types, each suitable for different applications and flow measurement requirements. These sensors are capable of detecting and measuring very small flow rates, usually in liquids or gases. Here's a breakdown of the most common types:
Turbine micro flow sensors work by measuring the flow rate of a fluid, in which the fluid flow causes a small turbine within the sensor to rotate. The speed of the turbine's rotation is directly proportional to the fluid's flow rate, and this is usually converted into an electronic signal. These sensors are appropriate to use when measuring clean liquids and gases, and they offer precise measurement in a high range of flow rates. Common applications are in the oil and gas industry and chemical processing.
Positive displacement flow sensors are flow-based metering devices that work by measuring the flow of fluids through sealed chambers. The fluid causes the chamber's gears or lobes to displace them, and the number of displacements is counted. Such sensors are accurate in measuring low flow rates and are ideal in applications requiring the measurement of viscous fluids. Their common usage is in food and beverage manufacturing and pharmaceutical industries.
Ultrasonic flow sensors work by sending and receiving ultrasonic sound waves through a fluid to determine its flow rate. The time it takes for the sound waves to travel through the fluid is affected by its flow, and this will then be calculated to determine its flow rate. These sensors are non-invasive and are usually applied in critical applications where the fluid must not be contaminated, like in the medical field. They measure both micro liquid flow sensor and gas flow rate and are ideal for various industries.
Capacitive flow sensors are devices that work by measuring changes in capacitance caused by the flow of a particular fluid. These sensors are sensitive to small flow rates and are non-invasive, measuring thick or thin fluids with solid content. These sensors are applied in the pharmaceutical industry to monitor fluid flow in production processes.
Thermal flow sensors work by measuring the heat transfer between a heated element and the fluid or gas flowing past it. When a fluid flows over a heated element, its temperature will drop, depending on its flow rate. This type of sensor is very sensitive to changes in flow rates and can also be used to measure both liquid and gas flows. This sensor is mostly used in HVAC systems, semiconductor manufacturing, and chemical processing.
The purpose of micro-flow sensors is to measure the flow rate and provide accurate flow data for process control, quality assurance, and equipment monitoring. In addition, micro flow sensor functionality will include the following:
Micro flow sensors are widely applied in different industries, as mentioned below, due to their sensitivity in measuring flow rates and greater versatility:
Micro flow sensors are designed with various features that will allow good performance, accuracy, and versatility in measuring low flow rates for liquids or gases. The following are the common features:
These sensors are designed to detect very low flow rates, which helps make them versatile in applications like biomedical devices and microfluidics. This high sensitivity ensures precise measurements in environments where small variations in flow can cause significant effects.
Micro flow sensors are compatible with a wide range of fluids and gases. This includes viscous liquids, chemicals, and air. Their material construction allows them to handle various applications across industries from pharmaceuticals to electronics manufacturing.
The majority of micro flow sensors provide digital outputs instead of analog signals. This enables their integration with advanced control systems and microprocessors, thus improving system responsiveness and accuracy of flow measurements.
Micro flow sensors are usually designed to work under extreme temperatures and pressures that are typical in many industrial processes. Enhanced durability ensures these sensors consistently perform well without degradation over time.
Micro flow sensors are designed, as the name suggests, in compact sizes. They are small enough to fit into tight spaces in portable medical devices or aerospace instruments. Due to their portability, these sensors can be installed in systems where space is really limited, but accurate flow measurement is still crucial.
The accurate measurement of flow rate depends on the proper calibration of microflow sensors. Most of these sensors come factory calibrated to ensure measurement accuracy right from installation. Some high-end models even allow for recalibration in the field, maintaining long term precision in various conditions.
Choosing the right micro flow sensor for applications will require evaluating several key factors that affect performance, compatibility, and overall measurement accuracy. Below are these key factors:
Determine if the application involves measuring liquid or gas flow. Some sensors are designed specifically for liquids or gases, while others have the versatility to measure either. Selecting a sensor with the right compatibility ensures accurate measurements that are within range of expected operating conditions.
Select a sensor with an appropriate flow rate measurement range. This range should encompass the minimum and maximum flow rates expected in the application. Choosing a sensor with the right range of measurements helps avoid dead zones and ensures the accuracy of the measurements across operating conditions.
Consider what the sensor will be used in for system compatibility. Different sensors will have different types of outputs. Some may be analog, while others are digital or pulse outputs, depending on the application and the control system used. Selecting a sensor with an output type that is easily integrated into existing infrastructure will simplify implementation and improve real-time monitoring.
Assess the ease of installation and maintenance requirements of the flow sensor. The sensors should ideally have straightforward mounting procedures and minimal maintenance needs. Factors such as seals or gaskets that require frequent replacement will impact long-term operations. Also, the ease of calibration and whether the sensor is robust enough for in-field adjustments will need to be considered.
Evaluate the sensor's materials of construction and design to ensure they can endure industrial processes. This includes assessing chemical compatibility with fluids or gases the sensor might come into contact with and its ability to sustain extreme temperatures and pressures.
A1: Micro flow sensors are used across a variety of industries to measure the flow rates of liquids and gases. Their high sensitivity enables precise flow rate detection, making them ideal for applications requiring advanced monitoring and control.
A2: These sensors find applications in medical, pharmaceutical, semiconductor, aerospace, and environmental monitoring industries. They monitor and control fluid flow in different processes to ensure efficiency, safety, and accuracy.
A3: Micro flow sensors use mechanisms like turbine rotation, positive displacement, or heat transfer to translate the flow into measurable signals. These signals are then converted to provide accurate flow rate data for the process in question.
A4: Micro flow sensors have the sensitivity to measure very low flow rates, provide real-time digital output, and can easily be integrated into modern control systems. They are also compact in design and suitable for various applications.
A5: Many micro flow sensors are designed to endure extreme temperatures, high pressures, and chemically aggressive substances, depending on their materials of construction. This makes them fit for numerous industrial applications where other sensors may fail.