
All categories
Featured selections
Trade Assurance
Buyer Central
Help Center
Get the app
Become a supplier

(173 products available)





























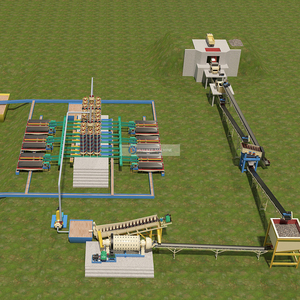
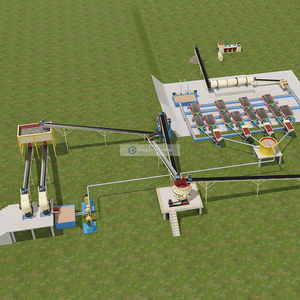









A kiln for mineral processing is a high-temperature furnace used to process minerals and produce materials such as cement, lime, and ceramics. There are various types of kilns with different designs suited for diverse mineral processing needs. Some of them are described below.
Rotary kiln
The rotary kiln is the most popular type of mineral processing kiln. It is a large cylindrical-shaped vessel that rotates slowly on its axis. The kiln is heated along its length to create different temperature zones. At about 3 to 4 meters wide and 100 meters long, rotary kilns are huge. Materials enter the higher end and move to the lower end while the kiln rotates. They are exposed to various atmospheric parts to achieve the desired chemical change.
For example, in cement production, limestone, clay, and iron are processed to produce clinker. Rotary kilns can also be used to produce ceramite and active lime.
Shaft kiln
The shaft kiln consists of vertical shafts where the mineral materials move downwards, while the airflow moves upwards. The airflow heats the material as it descends through the shaft. Shaft kilns are typically used for producing lime, cement, and other minerals that require a continuous process. They have a simple structure and are more energy efficient than other types.
Unlike rotary kilns that have several heating zones, shaft kilns have a single heating zone, so they are less efficient when it comes to fuel usage. The mineral material must be grounded to a fine powder, which may not be ideal for all cement production companies.
Vertical kiln
A vertical kiln has an oval or circular cross-section, and it tapers downwards. Material loading and airflow happen at the top of the kiln. At the bottom, ash exits the kiln. Vertical kilns are more productive than rotary and shaft kilns. They can also use different types of fuels and offer good quality output. However, vertical kilns can only be used for a limited number of minerals.
Solar kiln
The solar kiln uses solar energy to dry minerals such as cement and ceramics. It has a solar collector that captures sunlight and converts it into heat. The heat is stored in a buffer system and released to the kiln to raise the temperature and process the mineral material.
This type of kiln is environmentally friendly, but solar energy may not be sufficient in areas that do not receive a lot of sunlight.
Kiln diameter/size
Rotary kilns come in a variety of sizes and diameters. The correct dimensions are often chosen based on the amount of material to be treated, the residence time needed, and the throughput required.
Kiln speed
The incline and rotation of the kiln promote material flow. For instance, a lime rotary kiln might have a 3-7% upward slope and rotated at 1-5 revolutions per minute. The kiln speed is adjusted according to the processing tasks.
Heating/cooling system
Indirect rotary kilns are used for low-oxygen or contaminant processing, while direct rotary kilns apply oxygen as required. The rotary kiln's temperature may exceed 1000 °C. Therefore, refractory liners made of ceramic or porcelain are used to protect the body from heat damage. Some rotary kilns may use a dual heating system of natural gas and electricity.
Productivity
Rotary kilns can produce anywhere from several hundred to several thousand tonnes of treated material each day, depending on their size and design.
Routine care and maintenance is important to ensure a rotary kiln's longevity, efficiency, and safety. Here are some common maintenance steps:
Regular visual inspection
Operators need to conduct inspections on rotary kilns to ensure their normal operations. It is vital to assess abnormal conditions or possible departments by using technology-assisted inspection methods and professional knowledge.
Condition monitoring
21st-century rotary kiln maintenance approaches focus on condition-based maintenance. They take the condition deterioration of parameters like temperature, vibration, and pressure as the basis of maintenance operations. This allows users to conduct the needed maintenance on time and schedule the maintenance.
Replacement of parts
Some key parts of the rotary kiln, like elastic coupling, combustion chamber, seals, etc., are prone to wear. They need to be replaced regularly to ensure the kiln functions normally.
Mineral processing refers to the extraction and beneficiation of valuable minerals from ore bodies. It's worth noting that certain minerals must be transformed before they can be utilized in various industries, such as the construction industry. This explains why there is a high demand for mineral processing at the heart of industry.
The mineral in question is often an unwanted rock that's obtained from the earth's crust. Once the kiln for mineral processing comes into play, a particular mineral (often limestone) is calcined to produce lime, a key ingredient when it comes to processing minerals. Different kilns can carry out this task, as well as a number of other benefits that come with processing minerals.
Whether it's a rotary kiln or shaft kiln, here's a more in-depth look at how mineral processing is utilized with the help of a kiln:
Producing Lime and Cement
The rotary kiln for lime calcination is a key piece of equipment in the lime industry. In the rotary kiln, limestone (calcium carbonate) is heated to high temperatures, which causes it to decompose into lime (calcium oxide) and carbon dioxide. The product of the rotary kiln is quicklime, which may be further processed into hydrated lime or caustic lime.
Rotary kilns are also used in the cement industry. Cement consists of calcium, silicon, aluminum, and iron. Cement producers usually use three different types of kilns: rotary kilns, shaft kilns, and cement ball mills. Rotary kilns are, however, the most common. Rotary cement kilns are divided into two parts: the calcining and roasting zones.
Metallurgical Processing
Metallurgical processing involves mineral transformation, which often requires rotary and shaft kilns. In metallurgy, different types of minerals are obtained, including ferrous minerals like iron ore and non-ferrous minerals such as copper, nickel, zinc, cobalt, and aluminum.
Some minerals may also be alloyed, for example, titanium, manganese, and chromium, in the iron and steel production process. The rotary kiln is used to preheat, heat, and reduce iron ore to produce "direct reduced iron" or "hot briquetted iron" that is strategically used in electric arc furnaces to manufacture steel. Rotary kilns are also used to produce ferronickel, an important alloy used in steelmaking.
Chemical Production
Various minerals are processed to produce chemicals such as soda ash, potassium carbonate, calcium carbonate, phosphoric acid, and citric acid, to name a few. Shaft kilns are typically used to produce soda ash (sodium carbonate) using the Solvay process.
Calcium carbide is produced by processing calcium carbonate (limestone) and petroleum or coal at very high temperatures in rotary kilns. Calcium carbide is commonly used to produce acetylene gas, which is then used for various applications, including welding and cutting steel.
Glass and Ceramics
Both rotary and shaft kilns are used in the glass and ceramics industry. A rotary kiln for glass production will produce raw materials at high temperatures to create molten glass. Once the glass kiln cools down, it will be shaped into various products to suit the needs of the industry. The shaft kiln used in the glass industry has an upward-flowing reverse draft - ideal for the production of fiberglass and wool.
In the case of ceramics, the rotary kiln will bake different types of ceramics at a high temperature. Once the ceramic kiln cools down, it will be formed into tiles, pottery, sanitary ware, tableware, refractories, and engineering ceramics.
Construction Materials
When it comes to construction, a kiln for mineral processing plays a crucial role by producing essential materials such as cement, ceramic, glass, and lime. Cement is the primary binder used in concrete, the most widely used construction material. Cement is produced using rotary or shaft kilns.
Lime may be classified as hydraulic or non-hydraulic limestone. It's used in many building materials, including lime mortars and plasters, lime-based concrete, and hydrated lime stabilized soil.
There are many different types of mineral processing kilns, each with its own unique features. When placing an order for reselling, buyers must ensure that their target customers would use the kind of kiln they want to order for.
Generally, processing equipment is available in different sizes. Customers looking to process minerals on a smaller scale would most likely be interested in a bench-scale kiln. This kind of kiln has a processing capacity of about 1 to 50 kilograms of material per hour. Bench-scale kilns also have the capability of processing several batches of materials continuously.
Businesses that process minerals in large capacities would need commercial-scale mineral processing kilns. These industrial-sized processing machines have a much larger capacity, typically in the range of 100 to 10,000 kilograms per hour. Commercial-scale kilns also have the ability to run continuously for extended periods, some up to several months without having to stop.
When buying a mineral processing kiln, it is very important to consider how energy efficient the machine is. Many suppliers have several energy efficient processing machines. Those that are energy efficient can easily translate into cost savings for customers in the long run. This is mainly because energy-intensive machines usually have a high energy consumption rate. It might be a good idea to start asking suppliers about the energy consumption rating of their processing machines and to compare it to that of other brands.
Since business buyers sell to customers with different needs, it isn’t easy to meet the needs of everyone. Buyers should look for suppliers that offer a wide variety of processing kilns to choose from. They should have different specifications, applications, construction materials, heating methods, etc., so that all types of customers’ demands can be satisfied.
Finally, buyers should also consider if the processing kiln they want to buy comes with any additional features and accessories. Additional features and accessories can enhance the performance of the processing machine and improve efficiency. Some valuable accessories include air flow controllers, temperature regulators, insulation systems, or dust collection systems. Discovering these kinds of accessories can also improve the customer experience and satisfaction level.
When looking for suppliers to partner with, buyers should ensure that the suppliers have processing machines of varying durability. They should offer processing machines constructed with different materials that boast varying lifespans. This way, buyers can get to cater to customers who demand high durability and those who don't.
Q1: What are the different types of mineral processing kilns?
A1: The different types of kilns include rotary kilns, vertical shaft kilns, tunnel kilns, and flash calcination kilns.
Q2: What are the trends in mineral processing kiln technology?
A2: The trends include energy-efficient designs, automated control systems, and construction using advanced refractory materials.
Q3: What are some mineral processing kiln safety practices?
A3: Some safety practices include proper ventilation, use of personal protective equipment, regular maintenance, and monitoring of emission levels.
Q4: Can one retrofit an existing mineral processing kiln?
A4: Yes, it is possible to retrofit an existing kiln. However, any such modification should only be done after a detailed analysis of the kiln's condition and capacity.