(60016 products available)















































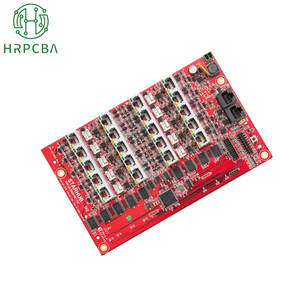
































































































































































An industrial robot controller is a computer used to control the movement and functions of an industrial robot. There are several types of industrial robot controllers.
Teach Pendant Controllers
A teach pendant is a handheld, lightweight device used to control and program industrial robots. It functions as the robot's "remote control" and is typically connected to the robot by a flexible, coiled cable. The teach pendant allows an operator to program the robot by guiding it to various points, teaching it those points, and then allowing the robot to repeat that motion in the same sequence without further assistance.
Smartphone Controllers
The smartphone controller takes advantage of the trend of using smartphones in other aspects of life, utilizing the wireless connectivity and interface of a mobile phone to create a new way of controlling the robot. This controller typically includes an application (app) developed for a specific robot that allows users to control and program the robot through their smartphone. Communication between the smartphone and the robot is usually done via Bluetooth or Wi-Fi.
Remote Controllers
A remote controller allows users to control the robot's motion and operation from a distance. This provides flexibility and convenience in controlling and operating the robot. Various wireless technologies, such as radio frequency (RF), infrared (IR), or Bluetooth, are typically used in remote control to enable the remote controller to send commands to the robot.
PC-Based Controllers
A PC-based controller is a type of robot controller that uses a personal computer (PC) as its core control unit. This means that the robot's control, programming, and management functions are implemented through a PC. The use of a PC-based controller provides high flexibility and functionality, allowing the user to customize and expand the robot's functions and capabilities as needed.
Industrial robotic controllers specifications can vary significantly based on different manufacturers and specific models. Here are some general specifications to consider.
Another essential thing to know about the robot controller is that it needs routine maintenance to ensure optimal performance and prolong its lifespan. Here are some maintenance tips to help end users take appropriate care of the robot controller.
The industrial robot controller plays an important role in various scenarios. Below are some of them:
Manufacturing industry
In manufacturing industries like automobile manufacturing, mechanical automation, electronics, etc., industrial robots are widely applied. The industrial robot controller can control the robots to carry out automated production processes such as assembly, welding, painting, packaging, and more, thus improving efficiency and quality.
Precision machining
In machining industries like CNC machining, the industrial robot controller can possess functions like tool change, workpiece change, loading/un unloading, etc. It can be used with precision machine tools for complex machining tasks.
Logistics and warehousing
In the field of logistics and warehousing, industrial robots can be used for automatic sorting, stacking, palletizing, depalletizing, and other tasks. The industrial robot controller can realize the automation and intelligence of these operations, thus promoting the efficiency and accuracy of logistics management.
Medical and healthcare
In the medical and healthcare industry, the industrial robot controller can control surgical robots, rehabilitation robots, drug dispensing robots, and more. It enables minimally invasive surgery, aids in patient rehabilitation, ensures medication safety, and provides other intelligent medical services.
Food and beverage industry
In the food and beverage industry, the industrial robot controller can be used for food processing, packaging, and bottling, among other tasks. It helps ensure food safety, hygienic standards, and intelligent production lines.
Research and education
In research and educational fields, industrial robot controllers are often used in experiment setups, laboratory automation, robotic competitions, and robot programming training, among other applications. They provide a platform for researchers and students to explore and practice robotics.
Before going into the details of different robot controllers, it is helpful to know the trends affecting how people are choosing controllers for their robots.
Compatibility and Connectivity:
People are looking for controllers that can easily link up with various sensors, actuators, and communication protocols. There is a high demand for open-source platforms and modular architectures, enabling customizable and scalable robotic solutions.
Usability and Programming:
More buyers are looking for user-friendly interfaces and programming environments that streamline robot control. They want intuitive visualization tools, simulation capabilities, and code libraries to expedite development and reduce time-to-market.
Integration of AI and Automation:
As artificial intelligence and automation advance, buyers seek controllers with built-in AI capabilities and support for machine learning algorithms. These controllers enable autonomous decision-making, adaptive behavior, and intelligent perception, enhancing the robot's functional richness.
Performance and Real-time Control:
Controllers with high processing power, low latency, and advanced control algorithms are in demand. Buyers prioritize controllers that can handle complex tasks, deliver precise motion control, and support simultaneous multi-robot operations, ensuring smooth and efficient robotic performance.
Compatibility and Communication:
Robot controllers are usually designed to work with specific robots. It's crucial to ensure the controller chosen will communicate well with the robot. Sometimes, a firmware update may be all that's needed for both parts to work together nicely. The controller and robot also need to share the same protocol. A common one used with industrial robots is TCP/IP, which helps different devices and systems talk and work together over regular computer networks.
User Interface and Programming:
A good robot controller should be easy to use and program. Look for a controller with a friendly, visual programming interface that lets users drag and drop tasks instead of just typing in commands. This kind of interface makes controlling the robot easier and helps new users learn faster. Controllers with simulation capabilities also allow users to visualize robot behavior before running it in real life, decreasing errors and making it easier to figure things out faster.
Scalability and Flexibility:
Controller selection should also look ahead to what might be needed later. The chosen controller now should work with different robot types and sizes in the near future. It should also easily integrate new sensors and tools that could be added to robots down the line. A controller with a flexible, modular design means it can change and expand along with growing business needs over time.
Performance and Reliability:
The robot controller must be powerful enough for the job, and its dependability is also critical. Customers' expectations are always rising, so it's vital to pick a controller that can handle demanding tasks while doing them precisely and consistently. It should have strong processing ability, low lag, and dependable stability under continuous heavy use. Choosing a reliable controller helps guard against breakdowns and loss of output in an increasingly competitive business environment.
Q1: How does an industrial robot controller work?
A1: An industrial robot controller works by receiving instructions from a program that defines the tasks the robot must perform. The controller interprets these instructions and sends commands to different robot components.
Q2: What are the trends in industrial robot controllers?
A2: The most notable trends in industrial robot controllers include the growing demand for collaborative robots, the increasing importance of flexible and scalable automation solutions, the rise of cloud-based robotics, and the emergence of artificial intelligence and machine learning in robotics.
Q3: Can an industrial robot controller be programmed?
A3: Yes, an industrial robot controller can be programmed. Robot controllers are typically programmable devices that can be programmed to perform various tasks.
Q4: What are the benefits of having a good industrial robot controller?
A4: The benefits of a good industrial robot controller include easy-to-use programming, high-precision control, versatility, integration capability, and reliable performance.