Understanding High Voltage Testers
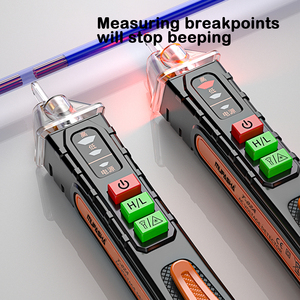
A high voltage tester is an essential device used primarily for testing electrical devices, insulation, cables, and various components to ensure safety and functionality in high voltage applications. These testers are crucial in confirming that electrical installations can handle the operational voltages before they are put into use, thus safeguarding both equipment and personnel.
Types of High Voltage Testers
- Analog High Voltage Testers: These testers use traditional analog displays to show voltage levels, providing a simpler interface.
- Digital High Voltage Testers: Equipped with digital displays, these testers offer more accurate readings and often include advanced features like data logging and small size.
- Insulation Resistance Testers: Specifically designed for measuring insulation resistance, these testers are vital in identifying potential electrical failures before they occur.
- Dielectric Strength Testers: Focused on measuring the dielectric breakdown of materials, these testers ensure that insulating materials can withstand high voltage without failing.
Functions and Features of High Voltage Testers
- Voltage Testing: High voltage testers are designed to accurately measure voltage levels, ensuring they meet specified standards.
- Insulation Resistance Measurement: They assess insulation quality by measuring resistance levels, identifying weak points that may cause failures.
- User-Friendly Interfaces: Most modern testers come equipped with intuitive controls and digital readouts for ease of use.
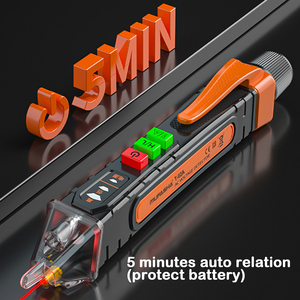
- Safety Features: Many high voltage testers include built-in alarms and auto shut-off functions to prevent operator injury.
Applications of High Voltage Testers
- Electrical Maintenance: Regular testing of equipment in substations, transformer stations, and other high voltage infrastructures to ensure continued safety and performance.
- Manufacturing: Used in the production stage for testing electrical components, including motors and circuit boards, to certify their operational efficacy.
- Construction: Verification of electrical installations in new buildings, ensuring compliance with safety regulations before energizing systems.
- Research and Development: Engineers use high voltage testers to assess new materials and designs, ensuring they can withstand operational stresses.
Advantages of Using High Voltage Testers
- Enhanced Safety: Prevents electrical failures that can lead to equipment damage or personal injury, thereby promoting a safer work environment.
- Cost-Effective: By identifying issues early, businesses can avoid costly repairs and downtime associated with electrical failures.
- Improved Performance: Regular testing maintains the integrity of electrical systems, ensuring they operate within desired parameters.
- Compliance with Standards: Facilitates adherence to industry regulations and standards, which can be critical for legal and operational reasons.
























































































































































































































































 浙公网安备 33010002000092号
浙公网安备 33010002000092号 浙B2-20120091-4
浙B2-20120091-4