
All categories
Featured selections
Trade Assurance
Buyer Central
Help Center
Get the app
Become a supplier

(22349 products available)



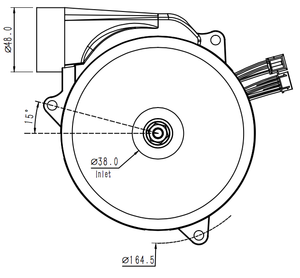
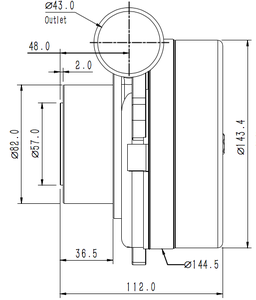
Market Overview: The global market for high temperature fans, a subset of the industrial and commercial fans sector, is witnessing robust growth. As of 2023, the overall market for industrial and commercial fans and blowers was valued at approximately $10.3 billion and is projected to reach $14.9 billion by 2030, representing a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.4% during this period, according to Global Industry Analysts. Notably, the U.S. market alone accounted for $2.7 billion in 2023, while China is expected to grow at an impressive CAGR of 8.2%, reaching $3.3 billion by 2030. This growth is largely driven by the increasing demand for efficient cooling solutions in high-temperature environments, such as manufacturing plants and heavy-duty machinery sectors, where operational efficiency is critical.
Industry Insights: The demand for high temperature fans is significantly influenced by industrial trends emphasizing energy efficiency and operational flexibility. As industries strive to reduce emissions and enhance fuel efficiency, the adoption of technologically advanced cooling solutions has become paramount. The rising awareness of environmental sustainability and the need for reliable cooling systems in fluctuating temperatures are key drivers of this market. Companies are also investing in research and development to create more adaptable fan systems that can respond to varying cooling needs, thereby extending the lifespan of equipment and reducing maintenance costs. This strategic focus on innovation is expected to further enhance market opportunities, particularly within niche sectors that require specialized cooling solutions, solidifying the position of high temperature fans in industrial applications.
High-temperature fans industrial are industrial fans that can work under high-temperature environments. According to different classification standards, they can be classified into different types.
By blade structure:
High-temperature centrifugal fans have an impeller that draws air from the fan's housing, and the rotating motion of the motor forces the air out through ducts. The direction of airflow of centrifugal fans are perpendicular to the axis of the impeller. High-temperature axial fans have blades that push air parallel to the axis of the motor and directly behind the motor. Both high-temperature centrifugal fans and axial fans are designed to resist long-term high-temperature environments.
By installation style:
High-temperature ducted fans are usually directly connected to the ventilation duct system. They are located inside or outside the equipment to extract or supply air to the duct network. Ducted high-temperature fans help to convey or extract air in the whole ventilation system. High-temperature blowers, on the other hand, usually have an open blade design. They are mounted in areas where concentrated airflow is needed. High-temperature blow fans are used to fan or push the air in a wide area.
By pressure:
High-temperature centrifugal exhaust fans are usually used to discharge the waste heat from high-temperature areas. They are located at the center of the high-temperature source. Moreover, high-temperature positive pressure fans increase the air pressure inside enclosed spaces to prevent the entry of external contaminants and low-temperature air. They create a safe and clean working environment for workers.
Industrial hot air fans are essential pieces of equipment for a wide range of industries that need to create or maintain high temperature and humidity levels in enclosed spaces.
The use of industrial high-temperature fans isn't limited to manufacturers and the food industry. Other industries and businesses use industrial high-temperature fans. Here are some of them:
Agriculture
High-temperature fans are used in poultry barns and greenhouses to help maintain high temperatures for plants and animals. In greenhouses, they can be used to ensure proper pollination of plants and provide adequate plant spacing. The high-temp fans also facilitate the transportation of nutrients and moisture to all parts of the plant. In addition to facilitating plant growth, high-temp fan units help prevent viral infections in poultry and livestock. The fans also help reduce ammonia buildup in barns, which can be harmful to both animals and workers.
Automotive Service and Repair
Automobile repair shops use high-temperature pedestal fans to help cars dry faster after a wash or detailing service. Sometimes, body shops also use high-temperature pedestal fans to speed up the curing process when they use certain chemicals, paints, or sealants on vehicles. Additionally, fans improve comfort for technicians working in tight engine spaces and around heat-generating components.
Construction
In the construction industry, high-temperature pedestal fans are used in two primary ways. First, they are used to ventilate high-temperature areas and prevent heat-related illnesses when construction work is done in high-temp areas. Second, the fans circulate and dry air rapidly to speed up the construction processes of certain tasks like concrete drying.
Warehousing and Distribution
Oftentimes, workers in warehouses have to deal with high heat and humidity levels that can impact both comfort and productivity. High-temperature pedestal fans are used to create a more comfortable working environment by cooling down warehouse staff and improving air circulation. The fans are also strategically placed around the facility to help with the rapid drying of floors after cleaning operations and incident spillages. Some warehousing facilities also implement the fans as a fire safety measure. This is because the fans can help to clear smoke from the building in the event of a fire.
Mining
The mining industry, especially underground mining, can get really hot and that leaves miners prone to heat exhaustion and heat strokes. Many mining companies use high-temperature pedestal fans to prevent miners from overheating when working in extremely hot conditions. The fans help them stay cool. Another way high-temperature mining fans are used is by preventing equipment from overheating. In addition to this, the fans improve the overall ventilation in the mining shafts and tunnels.
When shopping for heavy-duty high-temperature cooling fans, it helps to have a checklist of the essential features to ensure the final product selection matches specific application needs.
Operating temperature:
Everyone's primary focus when buying high-temperature cooling fans is typically the maximum operating temperature. However, it's just as important to consider the ambient temperature of the application site. The ambient temperature could influence the fan's performance and lifespan.
Airflow:
Flow is the amount of air in cubic feet moved by the fan per minute (CFM). The airflow a high-temperature fan offers needs to be sufficient enough to cool the hottest components in the application. However, it should be noted that more isn't always better when it comes to the CFM rating. A fan with an excessively high CFM could create too much force and disturb the surrounding environment and pressure.
Fan speed control:
Some high-temperature fans come with a provision to control their speed. This feature enables the user to adjust the fan's speed according to the specific cooling needs of the moment. It's important to consider the simplicity and safety of the control method. Also, think about the application's need for different fan speeds.
Noise level:
High-temperature fans are typically rated according to their noise output in decibels (dB). The noise level a fan produces could be the difference between a peaceful working environment and an employee complaining about annoying fan noise. While it's impossible to completely eliminate the noise a fan makes, it's possible to choose one with a design that minimizes it.
Material and build quality:
Given the harsh conditions a high-temperature cooling fan will be subjected to, it's vital to select one built with durable materials. The construction of the fan should also be robust enough to withstand extreme temperatures, vibrations, shocks, moisture, and corrosive substances.
Warranty and support:
A high-temperature fan's warranty and the support offered after purchase can offer some peace of mind. The warranty protects buyers from the risks associated with an early fan failure. It also allows users to get the support they need whenever they have any issues with the fan.
Q1: How powerful are high-temperature exhaust fans?
A1: The power of high-temperature exhaust fans can vary depending on the design and intended use of the fan. They can range from small power ratings around 100 watts to more significant power ratings such as 500 watts, 1000 watts, or even higher for industrial-grade exhaust fans.
Q2: What material is used for high temperature blower fan?
A2: High-temperature blower fans are typically made from materials that can withstand high temperatures and maintain their structural integrity. One common material used for high-temperature blower fans is reinforced plastic or FRP (Fiber Reinforced Plastic). Some might use stainless steel.
Q3: What temperature do high temp fans operate?
A3: High-temperature exhaust fans are designed to operate in environments with elevated temperatures. The specific temperature rating can vary depending on the design and intended use of the fan. Many high-temperature exhaust fans are designed to operate continuously at temperatures up to 200°C to 260°C.