
All categories
Featured selections
Trade Assurance
Buyer Central
Help Center
Get the app
Become a supplier

(1243 products available)
































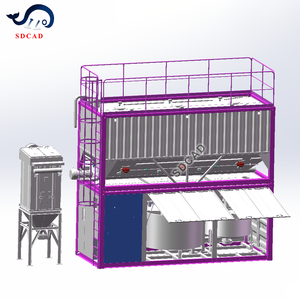












A grout batching plant is a machinery used to mix various components of grout. The grout batching plants are used to prepare the grout in consistent and precise proportions. There are several types of grout batching plants that feature distinct functions and specifications.
Wet
Wet grout plants prepare pre-mixed grouts that can be sold in bulk or used at the grout plant's location. When using this type of plant, the customer has to make sure that the bulk pre-mixed grout is the right product for their application, and then they can have it delivered and reduce costs and labor.
Dry
Dry grout plants batch, blend and store dry material until it is time to fill the truck or bulk bin. Many of these plants have computerized the entire process with minimal to no human interaction at any stage. They can be programmed to mix a certain recipe that can be used in a particular model of a concrete pump.Costs can be reduced significantly with a dry batch plant because water is not included in the mixing process and the weight of the material being shipped is less.
Partial
A partial wet batch plant is a hybrid model that can make both wet and dry batches. This style of the plant is excellent for companies who want to have the versatility to produce both types of grout. Employees must be adequately trained at the facility to know how to make the grout for it to be safe and effective.
Prepackaged vs on-site mixing
This distinction has been made now that many companies use pre-packaged cement and concrete products instead of producing their own. It doesn't always make sense to have the concrete cement plant on-site. Some companies are far away from a plant, and some businesses prefer to store the cement overhead rather than in bins next to the grout plant. On-site mixing is almost always more cost-effective than the expense of having the materials shipped to the site, and buyers can save on delivery fees.
Belt vs. central mix
A central mixing plant is one where all of the materials are mixed in a giant vat, usually with computer programs that can mix the grout to exact specifications. A central-mix grout batch plant has all the vital ingredients of the cement, aggregate, and water fed into it, typically in large quantities. It is then revolved in a drum or central mixing container, either at the site of the plant or in transit to the site where it will be used. This drum does not need any baffles or grooves because the mixing time is so long that the cement will not need to be re-mixed after it has been poured out. Central-mix plants can produce boards within an hour and approximately 150,000–200,000 pounds of material in a year.
Belt vs. dome storage
The primary method of aggregate transportation in a grout batching plant is through the use of conveyors or belts that move aggregate (material ranging from gravel to sand) from a quarry or stockpile to a storage bin or silo at the processing facility. The benefit is that the aggregate is not split at any time, and no dust settles onto it. Some plants use dome storage facilities because of the ability to control temperature inside the dome, which means monitoring and regulating the amount of moisture in the cement.
Grout Capacity:
The capacity of a grout batching plant specifies the maximum amount of grout it can produce in a single batch. Typically, this is measured in liters or gallons.
Production Rate:
The grout plant's production rate refers to how quickly it can produce grout. This is usually measured in batches per hour or tons per unit of time. The production rate depends on many factors including the plant's size and the mixing speed.
Materials Handling System:
Grout plants often have different methods for handling materials, such as weighing hoppers, conveying systems or pneumatic conveying. The style and capacity of the materials handling system can affect the accuracy and efficiency of grout production.
Automation and Control System:
Modern grout plants often use automated control systems to manage production and recipes. These control systems may include touch screens, programmable logic controllers (PLCs) and data recording functions. The level of automation and control system functions can affect the quality and consistency of the grout.
Regular Cleaning:
Clean the entire equipment surfaces and containers of the grout mixing plant. This can prevent cross-contamination and accumulation of residues.
Checking:
Regularly check all parts of the equipment, such as screws, bolts, seals, etc. This can ensure the stability and tightness of the device, preventing leaks or loosening.
Lubrication:
Add lubricating oil to the moving parts of the equipment as required. It can keep the smooth operation of the mixing plant, reducing the abrasion of the equipment.
Replacement and Maintenance of Wearing Parts:
Regularly replace and maintain the worn parts of the grout plant, such as mixers, pumps, conveying pipes, etc. This can maintain the stable operation and product quality of the equipment.
Inspection:
Inspect the electrical system and control components of the equipment regularly. This can ensure the normal operation of the electrical system and control functions.
Regular Maintenance:
Carry out regular maintenance for key parts and components of the grout mixing plant, such as cleaning, adjustment, and calibration of the mixers, pumps, valves, etc.
Overall Maintenance:
Periodically conduct overall maintenance for the entire grout mixing plant. This may include cleaning of the entire equipment, replacement of key components, inspection and adjustment of the hydraulic system, electric drive system, etc.
The demand for grout mixing plants is increasing due to the continued growth of the construction industry. Many plant managers and construction companies opt for large-capacity batching plants to handle numerous projects at once. Here are some scenarios where grout batching plants are commonly used in the construction industry.
Large Infrastructure Projects
Grout batching plants are ideal for large infrastructure projects such as constructing bridges, dams, and tunnels. Such projects require high volumes of consistent, high-quality grout.
Deep Excavations and Anchoring
Grout is widely used for soil stabilization-anchored deep excavation support as well as dewatering techniques. Moreover, drilling anchors often use grout to create secure bonds between the anchor and the soil or rock formation. Therefore, using a mobile grout mixing plant will ensure the consistency and quality required for effective soil stabilization solutions.
Ground Improvement
Ground improvement techniques, such as mixing grouting and soil, require large volumes of high-quality grout. Therefore, a grout mixing plant on-site will provide the necessary material.
Precast Concrete Manufacturing
Precast concrete components use cementitious grout to fill voids and provide structural consolidation. Using a grout plant can help manufacturers achieve rapid production rates and maintain consistent quality.
Wet Plant Resistance Repairs
A grout batching plant can produce the repair needs of grouting. These include bonding repairs, hydraulic repairs, and anchorage repairs. Also, grout plants can carry out preventive repairs instead of being reactive to repairs that could end up being more costly.
When choosing a grout mixing plant, there are a few things to consider for people who are looking to invest in the best solution for their needs.
Assess specific requirements and project types
It's important to evaluate the types of projects that will be using the batching plant on a regular basis and the specific materials that will need to be mixed. Consider the size and capacity of the plant that will be needed to meet project demands.
Examine key features and technologies
Look at the features of the plant, such as its mixing speed and accuracy, as well as the advanced technologies it comes with that help to improve efficiency and quality.
Consider flexibility and scalability
It may be a good idea to go for a batching plant that has the capacity to handle a wide range of mixes and can be easily modified to accommodate changing project requirements in the future.
Think about automation and control systems
Apart from easy-to-use controls, it's important to look for plants with computerized batching capabilities that ensure precise measurement and consistent mix quality.
Pay attention to environmental considerations
Make sure to choose a plant that has sustainable features, like low emissions and efficient material utilization, that will help to minimize the impact of construction activities on the environment.
Look for solid after-sales service support
Finally, remember it’s important to select a reputable supplier that offers reliable technical support and comprehensive maintenance services for the plant in question.
Q1: How does a grout batching plant work?
A1: A grout mixing plant combines several raw materials to create grout. It transports the raw materials to the mixing machine, where they are combined to form a uniform mixture. The plant then stores the grout in a storage facility or silo, from where it is pumped or transported to the desired location.
Q2: What are the components of a grout batching plant?
A2: The components of a grout plant typically include a cement silo, a water supply system, a mixing unit, a storage facility or silo, a pumping system, and a control system.
Q3: What types of grout can be produced in a grout plant?
A3: Different types of grout plants are available depending on the mixing capacity. Some common types of grout are cementitious, polymer-based, epoxy, and sodium silicate grouts.
Q4: What are the advantages of using a grout mixing plant?
A4: The benefits of a grout mixing plant are: high production capacity, uniformity and consistency of the grout, quality control, adaptability to different types of grout formulations, and efficient supply for large-scale projects.