(992 products available)







































 Ready to Ship
Ready to Ship





































































































































































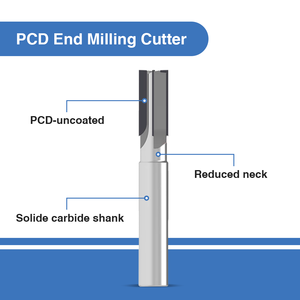
Graphite milling cutters have different types, each with unique characteristics and purposes. The cutters come in solid, carbide-tipped, and ceramic materials and are used for diverse milling applications.
Solid graphite cutters
Solid carbide graphite milling cutters are made of durable and wear-resistant materials for long-lasting precision. The cutters are significantly harder and more resistant to heat than steel and over 60% harder than titanium. Solid carbide cutters often have fine teeth for milling intricate graphite workpieces.
Carbide-tipped cutters
Carbide-tipped cutters combine steel bases with carbide tips, reducing costs while maintaining cutting efficiency. They are suitable for light to moderate milling operations. Users should look for carbide-tipped cutters with high-quality bonding between the tip and base for stability in prolonged use.
Ceramic graphite milling cutters
Ceramic cutters have unmatched hardness and thermal resistance, making them ideal for high-speed milling operations in graphite. The exceptional hardness enables sustained performance even at extreme temperatures. Buyers considering ceramic cutters should ensure compatibility with their milling machines, as these tools often require specific operational parameters.
Graphite milling cutters have varying industrial applications. They range from electronic components to aerospace industries, delivering precision cutting and shape advantages over traditional materials like tungsten or high-speed steel alloys. Here are some of the industrial applications:
Machining precision components in the electronics industry
In the electronics sector, graphite milling cutters shape and machine parts like heat sinks, circuit boards, and connectors. Advanced cutting technology allows the production of units with intricate designs and close tolerances to fit sophisticated electronic systems. The resistances of the cutters to heat and electricity limit damage during cutting, ensuring component performance and reliability.
Milling graphite in the automotive industry for brake linings and sensors
In the automotive industry, the cutters machine brake linings, gaskets, and sensors. The lightweight and strong brake linings made with graphite milled cutters improve braking systems' performance and longevity. In addition, the automotive gaskets and seals milled with graphite cutters accommodate efficient operation and engine longevity.
Milling in the aerospace industry for lightweight components
By machining components like seals, gaskets, and bushings, aerospace benefitted greatly from the intensive-precision-ceramic-milling-cutters. Aerospace parts made with graphite are significantly lighter and more durable compared to those made with traditional materials. The aerospace industry relies on graphite milling cutters to produce high-performance components that would be unsuitable for heavy vehicles.
Milling in the medical industry for surgical instruments and implants
The medical industry relies on the precision of graphite milling cutters in the production of crucial components like surgical instruments, implants, and diagnostic equipment. The non-magnetic and radiolucent properties of graphite make it ideal for surgical instruments. It allows doctors to perform operations under imaging without interference.
Milling in the energy industry for battery components
Graphite milling cutters are extensively used in the energy industry for battery components like electrodes. Their ability to produce intricate designs while maintaining tight tolerances makes them indispensable for enhancing battery performance. The non-metallic nature also allows for lightweight, energy-efficient designs ideal for portable power solutions.
Relevant product specifications and features of the graphite milling cutter are important to understand before purchasing and using the product and its industrial applications. Graphite milling cutters have specifications based on specifications like material composition and cutter geometry and features like coatings and cutter types. Knowing the specifications also helps in product maintenance, reducing machine downtimes and increasing operational efficiency.
Find the ideal material composition based on application
Graphite cutter material composition affects hardness, wear resistance, and toughness. Solid carbide cutters possess high hardness and resist wear and tear; hence, they are ideal for precise and extended operations. Ceramic cutters are suitable for high-speed milling operations due to superior heat resistance. Cobalt chrome cutters have great toughness and are suitable for operations where shock or impact is present.
Choose the ideal diameter based on machine specifications
The diameter of the graphite milling cutter should be compatible with the buyer's milling machine and should depend on the type of project to be undertaken. Larger diameter cutters are suitable for heavy industrial milling operations, while smaller diameter end mills are ideal for detail works such as engraving or precision machining of small parts. The diameter must also not exceed the machine's speed limit.
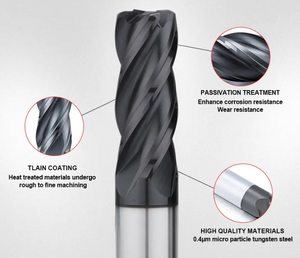
Select the ideal coating to improve durability
Coatings like TiN, TiAlN, and DLC reduce friction and increase the cutter's resistance to heat and wear, improving the cutter's durability. Titanium nitride is a good option for general-purpose milling. It is tough and wear-resistant. Titanium aluminum nitride is ideal for high-performance milling of hard materials. It has a high heat resistance. The amorphous diamond coating has an unmatched durability and chip-saving feature ideal for extended usage without wear on the cutter.
Ensure cutter geometry is compatible with the milling machine
Different mills have different cutter geometty. Ball end mills are suitable for finishing and contouring and are typically used in 3D milling operations. Flat end mills are used to clear the surface materials and machine flat features. Tapered end mills are suitable for sloped surfaces and tool paths. Finishing end mills have four to five flutes that can easily and smoothly mill already machined surfaces.
A. A graphite milling cutter is non-metallic and 70% less dense than copper, making it ideal for lightweight industrial applications. It is electrically conductive and resistant to corrosion. Compared to carbide cutters, graphite cutters are less brittle and tougher and can absorb shock.
A. Regular maintenance of a graphite cutter involves cleaning after each use, checking for wear and damage, inspecting the coating, regularly measuring sharpness, and storing the cutter in a dry and cool place synthetically free of dust. No maintenance must be done to the cutter during operation, as it will affect the working surface.
A. To extend the life of the cutter, avoid excessive pressure that can damage the cutter or wear it out. Regularly clean the cutter after each use to remove any residue that will clog the cutter. Store it in a dry and cool place devoid of dust. Use the cutter at the recommended speed and feed rate; do not exceed.
A. The industries that benefit from a graphite cutter include electronics, automotive, aerospace, medical, and energy industries. The non-metallic material makes it ideal for components that require high precision without weighing down the component.