(9840 products available)










































































































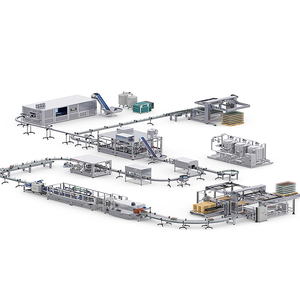






























































































A fully automated production line, also known as a fully automated manufacturing line, is a set of workstations and machines that processes materials and assembles products with little or no human intervention. Fully automated production lines are generally used for high-volume operations and tend to reduce labor demand while improving productivity, product consistency, and safety. Fully automated production lines are divided into five major categories. They all have distinct features and functions in an industrial setting.
Specs of a fully automated production line vary based on the factory's needs and the products being made. Here are some typical specifications for fully automated production lines:
Automated production lines need regular maintenance to ensure they're working well, helping with productivity, and minimizing breakdowns and disruptions. Here are some maintenance tips:
Fully automated production lines are widely used in various industries due to their efficiency. Here are some typical usage scenarios of a fully automated production line.
Food Industry
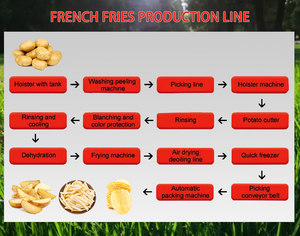
In the food industry, fully automated production lines are used for raw material processing, cooking, assembly, packaging, quality inspection, and other tasks. Fully automated production lines can achieve high-volume production, ensure product consistency, and reduce labor costs.
Automotive Industry
In the automotive industry, fully automated production lines are extensively used for vehicle assembly, including body framing, painting, installation of parts, and final inspection. Automation improves production efficiency, assembly precision, and product quality, meeting the high demands of the automotive industry.
Electronics Industry
Fully automated production lines are widely used in the electronics industry for the assembly of electronic components, circuit boards, and final product assembly. Automation improves production speed, accuracy, and efficiency, meeting the rapid production needs of the electronics industry.
Textile and Garment Industry
In the textile and garment industry, fully automated production lines are used for weaving, printing and dyeing, garment manufacturing, and other processes. Automation improves production efficiency, reduces labor intensity, and ensures product quality, meeting the demands of large-scale production.
Packaging Industry
The packaging industry adopts fully automated production lines for filling, sealing, labeling, and packaging. Automation improves production speed and efficiency, trains tedious manual operations, and meets the high demands of the packaging industry.
Plastic Industry
In the plastic industry, fully automated production lines are used for plastic injection, blow molding, extrusion, and other processes. Automation improves production efficiency, product consistency, and high precision, meeting the demands of large-scale production.
Business analysis
Analyze the business first. Look into the present production line and the spot areas where automation may aid in improving product quality, increasing capacity, or decreasing operating expenses.
Production volume and scalability
A fully automated production line may be a better choice if the required production volume is large. Automation provides the potential for expansive scalability, enabling rapid and simple expansions to meet rising production demands.
Flexible automation versus fixed automation
Automation lines that can handle a range of products rapidly and easily are flexible automation. On the other hand, fixed automation is better for processes that need constant production of the same product. Businesses should consider which kind of automation better suits their needs and choose it accordingly.
Integrated systems
Consider the possibility of automated production lines tightly connected to other operational activities—everything from supply chain and inventory management systems to customer relationship management software.
Cost of automation
A capital investment is required to set up an automated production process, so an essential cost analysis is required, taking into account installation costs, ongoing maintenance and energy requirements, and anticipated returns on investment from efficiency gains.
Supplier identification
Research system suppliers that are widely known and their reputations. Consider their level of global reach, their system's variety, and the level of after-sales support they provide.
Custom production lines
Some companies need a fully automatic production line constructed to meet their needs due to particular production requirements. These companies must look for vendors with the experience and capacity to design custom production lines and guarantee that the created solutions meet their specific technical requirements and quality standards.
Testing and quality assurance
Fully automated testing and quality assurance should be integrated throughout the production line. For instance, sensors, cameras, and AI technology can be used to watch and analyze the production process in real time to find errors and ensure product quality.
Employee training
Although automation decreases the need for some human labor, people still play a crucial role in overseeing, maintaining, and troubleshooting automated systems. Therefore, production lines that are fully automated should provide employees with the knowledge and training they need to work with advanced technical systems.
Sustainability considerations
Consider sustainability system design in supply chains that are totally automated. Fully automated production lines must include energy-saving and green practices, including recycling, reduced material waste, and effective energy utilization, to meet the demands of sustainable development.
Q1: What is a fully automated production line?
A1: A fully automated production line is a manufacturing system that uses machines and technology to do all the work without needing people.
Q2: What are the key components of a fully automated production line?
A2: The key components of a fully automated production line include conveyor systems, machinery and equipment, control systems, robotics, and quality assurance and inspection systems.
Q3: How does a fully automated production line work?
A3: In general, a fully automated production line works in three steps. First, materials and parts are delivered to the production line. Next, machines, tools, and robotics transform and assemble these materials and parts into finished products. Finally, products are inspected for quality, then packaged, and sent out.
Q4: What are the benefits of a fully automated production line?
A4: The benefits of a fully automated production line include increased efficiency and productivity, lower labor costs, improved product quality and consistency, enhanced workplace safety, and greater flexibility and scalability.
Q5: What industries use fully automated production lines?
A5: Fully automated production lines are commonly used in industries such as automotive manufacturing, electronics assembly, food and beverage processing, pharmaceuticals, and packaging.