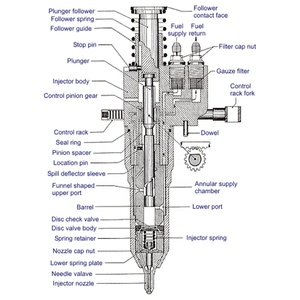
Types of Diesel Injector Nozzle
A diesel injector nozzle is a critical component attached to the end of the fuel injector in a diesel engine. Its primary purpose is to deliver atomized fuel into the combustion chamber. The nozzle contains tiny holes (injection orifices) that spray fuel in a fine mist, improving the air-fuel mixture for more efficient combustion and better engine performance. Regular maintenance and timely replacement are essential to maintain optimal engine function.
Single-Standard Nozzle
The most common type with a single set of injection orifices that spray fuel directly into the combustion chamber.
Best for: Small diesel engines in cars and light trucks
Advantages: Simple design, cost-effective manufacturing
Limitations: May not provide optimal fuel atomization
Multi-Hole Nozzle
Features multiple sets of orifices (typically 3-9) that create several fine fuel sprays for improved atomization.
Best for: Modern diesel engines with turbochargers or intercoolers
Advantages: Better air-fuel mixing, uniform fuel distribution, improved engine performance
Benefits: Reduced emissions and enhanced fuel economy
Piezoceramic Nozzle
Utilizes piezoceramic materials that generate mechanical stress when voltage is applied, controlling injection orifices.
Best for: High-pressure fuel injection systems
Advantages: Precise and rapid control of fuel injection, enhanced atomization
Limitations: More expensive due to complex design and advanced materials
Variable Nozzle
Designed to adapt to different engine operating conditions by adjusting orifice size and number.
Best for: Advanced diesel engines with common rail systems
Advantages: Optimized fuel injection across various operating conditions
Limitations: Complex design and higher cost limit use in simpler engines
Expert Tip: When selecting a diesel injector nozzle type, consider your engine's specific requirements, driving conditions, and performance expectations. Modern engines typically benefit most from multi-hole or piezoceramic designs despite their higher initial cost.
Specifications and Maintenance of Diesel Injector Nozzle
Understanding the technical specifications of diesel injector nozzles is crucial for proper selection and maintenance. These specifications directly impact engine performance, fuel efficiency, and emissions.
Measured in liters per minute, the flow rate determines how much fuel the nozzle delivers. This directly affects the engine's power and torque output.
Indicates how many fuel streams are emitted from the nozzle. Modern diesel engines typically have nozzles with 4-9 holes, depending on the engine design and requirements.
Measured in micrometers, the size of the holes critically affects fuel atomization. Smaller holes produce finer mist for better combustion, while larger holes create coarser droplets.
Measured in pascals or bar, higher injection pressures result in better fuel atomization and improved engine performance. Modern systems operate at extremely high pressures.
Expressed in degrees, the spray angle determines how fuel distributes within the combustion chamber, affecting the combustion efficiency and emissions.
Common materials include stainless steel, hardened steel, and ceramic. Material selection affects durability, wear resistance, and performance under high-pressure, high-temperature conditions.
Essential Maintenance Practices
Proper maintenance of diesel injector nozzles is crucial for optimal engine performance, fuel efficiency, and longevity. Follow these key maintenance guidelines:
| Maintenance Practice | Frequency | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Use quality fuel with cleaning additives | Every refueling | Prevents carbon buildup and maintains injector cleanliness |
| Replace fuel filters | Per manufacturer's schedule or every 15,000-30,000 miles | Traps contaminants before reaching injectors |
| Professional fuel system inspection | Annually or at 30,000-mile intervals | Early detection of potential issues |
| Monitor performance metrics | Continuously | Detects changes in efficiency, power, or emissions |
| Follow manufacturer service schedule | As recommended | Ensures optimal injector function throughout lifecycle |
| Avoid engine overloading | Always | Reduces premature wear on injector components |
| Use manufacturer-recommended fuel | Every refueling | Provides proper lubrication and cleaning properties |
Warning: Running your diesel engine on contaminated fuel or with clogged injector nozzles can lead to significant performance issues, increased emissions, and potentially costly repairs. Always prioritize proper maintenance and use high-quality fuel.
How to Choose Diesel Injector Nozzles
Selecting the right diesel injector nozzle requires careful consideration of your engine specifications, performance requirements, and operating conditions. The following factors are critical in making an informed decision:
Key Selection Criteria
| Selection Factor | Considerations | Impact on Performance |
|---|---|---|
| Engine Type | Light-duty vs. heavy-duty applications | Determines fuel flow requirements and atomization needs |
| Performance Standards | Emission regulations and performance goals | Affects nozzle design selection to balance power and emissions |
| Fuel Type | Standard diesel vs. biodiesel blends | Influences material selection and nozzle specifications |
| Quality & Compatibility | OEM vs. aftermarket options | Determines reliability, longevity, and system integration |
| Driving Conditions | City driving vs. highway vs. heavy load | Affects optimal nozzle type and specifications |
| Budget Constraints | Initial cost vs. long-term value | Balances quality considerations with financial limitations |
Expert Advice: While it might be tempting to choose less expensive aftermarket nozzles, OEM injector nozzles are specifically designed for your engine's requirements. The investment in quality nozzles typically pays off through improved performance, fuel efficiency, and reduced maintenance costs over time.
When balancing performance, efficiency, and emissions control, consider consulting with a diesel specialist who can provide guidance based on your specific engine model and usage patterns. Remember that the optimal choice varies significantly across different diesel engines and applications.
How to DIY and Replace Diesel Injector Nozzles
Replacing diesel injector nozzles can be challenging but is achievable with the right tools and careful attention to detail. This DIY guide walks you through the process step by step.
Essential Tools
Wrenches, sockets, screwdrivers, and pliers for disassembly and reassembly
For precise tightening of fuel system components to manufacturer specifications
Specialized tool for safely removing injectors without damaging components
For replacing nozzles in the injector body with proper alignment
Always use quality replacement parts compatible with your engine model
Clean rags, brake cleaner, and compressed air for workspace cleanliness
Step-by-Step Replacement Process
- Locate the Injectors - Remove the engine cover to access the diesel injectors. They're typically located on top of the engine block, with 4-6 injectors in most engines.
- Disconnect Fuel Lines - Carefully disconnect the diesel fuel lines from the injectors using an appropriate wrench. Be prepared for some fuel spillage.
- Remove Injectors - Loosen the nuts securing the diesel injectors in place. Use an injector puller to safely extract the injectors from the engine without damaging them.
- Replace Nozzles - Once removed, carefully detach the old nozzle from each injector and replace it with a new one using a filling tool to ensure proper installation.
- Reinstall Injectors - Return the injectors with new nozzles to their respective locations in the engine. Use a torque wrench to tighten the securing nuts to the manufacturer's specifications.
- Reconnect Fuel Lines - Reattach the diesel fuel lines to the injectors, ensuring all connections are secure and properly sealed to prevent leaks.
- Test Engine - Start the engine and observe its operation. Check for fuel leaks, unusual sounds, or performance issues that might indicate improper installation.
Important Safety Note: Always work in a well-ventilated area when handling fuel system components. Diesel fuel is flammable and potentially harmful. Wear appropriate protective gear including gloves and eye protection. If you're uncertain about any step in the process, consult a professional mechanic.
Questions and Answers
The replacement interval for diesel injector nozzles varies based on several factors including fuel quality, driving conditions, and engine design. Unlike some components, there isn't a set mileage or time interval for replacement. Instead, monitor for signs of wear or performance issues. With quality fuel and proper maintenance, nozzles in modern diesel engines can last 80,000-100,000 miles or more. Regular fuel system inspections by qualified technicians can help identify when replacement becomes necessary before major performance issues develop.
Several symptoms indicate potential problems with diesel injector nozzles:
- Poor Engine Performance: Reduced power, hesitation during acceleration, or rough idle
- Increased Fuel Consumption: Noticeable decrease in fuel economy
- Exhaust Smoke: Excessive white, black, or blue smoke from the exhaust
- Starting Issues: Difficulty starting the engine, especially when cold
- Engine Knocking: Unusual sounds or vibrations from the engine
- Failed Emissions Tests: Higher than normal pollution levels
- Uneven Running: Engine misfires or runs unevenly at various speeds
If you notice any of these symptoms, it's advisable to have your fuel system inspected by a qualified technician to determine if injector nozzle issues are the cause.
Once a diesel injector nozzle is damaged or severely worn, repair is generally not possible or economically viable. The precision engineering and tight tolerances of modern injector nozzles mean that any damage compromises their function. The only effective solution is replacement with a new nozzle. Some injector bodies can be rebuilt with new nozzles and internal components, but the nozzle itself is considered a consumable part that must be replaced rather than repaired when worn or damaged.
Common rail and unit injector systems represent different approaches to diesel fuel injection technology:
| Feature | Common Rail System | Unit Injector System |
|---|---|---|
| Fuel Pressure Source | Centralized high-pressure pump feeding a common rail | Each injector contains its own pumping element |
| Pressure Maintenance | Constant high pressure maintained in the rail | Pressure generated on-demand by each injector |
| Injection Control | Electronic solenoid or piezo valves in each injector | Mechanical or electronic actuation of the injector |
| Typical Applications | Modern passenger cars, light and heavy-duty vehicles | Older heavy-duty engines, some VW/Audi TDI engines |
| Key Advantages | Precise injection timing, multiple injections per cycle | Simplified fuel delivery, high injection pressures |
Common rail systems have largely replaced unit injector designs in modern vehicles due to their superior flexibility in controlling injection parameters, which helps meet stricter emissions standards while maintaining performance.