
All categories
Featured selections
Trade Assurance
Buyer Central
Help Center
Get the app
Become a supplier

(3416 products available)



















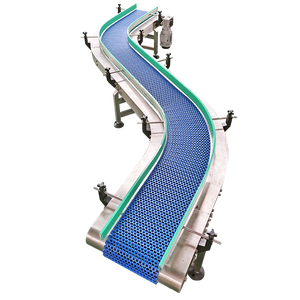


























Cleated Belt Conveyor-Horizontal Belt
A horizontal cleated conveyor belt is primarily used in packaging and production lines to convey materials over long distances. It maintains a steady, flat surface with effective cleat application for bulk and bagged materials. Their uncomplicated construction supports easy upkeep, and their versatility accommodates different load types. Power necessities depend on load weight and distance, ensuring energy-efficient transfer. In packaging and material movement, horizontal cleated belt conveyors excel due to low inclination and length, boosting productivity with dependable operation.
Cleated Belt Conveyor-Angle Belt
The angled cleated conveyor belt is necessary when moving goods across moderate to steep inclines. Angled cleats provide better grip and are appropriate for bulk, bagged, and packaged products in most industries. The angled design helps uptight field cloths from slipping, making it sensible in restricted spaces. The belt is durable, with every kind bearing heat, moisture, and abrasive materials. Heavy-duty angled cleated conveyor belts are available for large products. These systems enhance vertical movement efficiency while wanting space.
Cleated Belt Conveyor- Express Belt
Express belt conveyors are designed for swift and smooth material transportation. They are ideal for high-speed transportation of light to moderate-weight products, mainly in packages, cartoned goods, or small parts. They have a low cleat profile, providing only slight elevation as a function to assist motion along an inclined plane. This design reduces lag time, increasing systole thickness flow. Due to their speed and efficiency, these belts are regularly used in distribution centers, moving assembly lines, and other high-traffic conveyor networks.
Cleated Belt Conveyor-Wire Reinforced
Wire-reinforced cleated conveyor belts provide huge strength and durability intended for industries that handle very abrasive materials or process occasions with increased demand. Cleats offer better traction, clamping for bulk items, heavy merchandise, or field cloth bundles. Wire reinforcement enhances tensile strength, sleeper length, and heat or dampness resistance. These belts are great for heavy-duty fields corresponding to mining, cement work, or metallurgical work. A proper great spot wire arms relating to the belt enhances its lifespan and performance within hazardous environments.
The major purpose of cleated conveyor belts is to move subject material and systems horizontally and at an angle securely. The cleats or raised sections of the belt spacer items separate, preventing slipping or toppling over. This approach is used to transport products in warehouses, factories, and distribution centers. Cleated belts handle bulk materials, packaged products, or irregularly shaped items depending on the industry.
Any cleated belt conveyor system must provide the flexibility needed to perform in industrialized applications. Cohesion of cleat type, height, spacing, and belt angle with user needs determines application success. The belt design should be based on operating requirements like load weight and incline angle.
Warehouse and Distribution Centers
Cleated belt conveyors are widely used at warehouses and distribution centres to transport packaged products. Their application is ideal for moving boxes, pallets, or other products up or down inclines and maintaining great load stability. They fit into automatic sorting and routing systems, increasing efficiency in order fulfilment processes. Using a cleated belt conveyor system eliminates manual handling, reducing time and labour costs while accelerating the whole system's performance and efficiency.
Food Industry
Cleated belts convey raw materials like grains, vegetables, and bulk ingredients. In the food processing industry, these belts have been used to move packaged goods such as boxes, bottles, and canned foods, especially on inclined surfaces. Special materials that make the cleated conveyor belts conveyers comply with hygiene and safety standards. It prevents the field material from slipping, thus keeping the unitary operation safe and meeting the hygienic constraints of the food field.
Mining and Agriculture
The mining agro's cleated belt conveyor moves bulk materials like coal, ores, and aggregates. Cleated rubber conveyor belts are well suited for this kind of work because they can be tough enough to withstand this work. Cleated belt conveyors move fertilizer, grains, and other bulk commodities in the Agri-Industry. Most of these products do not come in packages, so it is critical to use a conveyor where the belt design will keep the product safely and securely in place during transportation.
Manufacturing Plants
Manufacturers use cleated belt conveyors to move their products from one section to another. In particular, they are necessary for transporting parts or products up or down inclines. In those joint work, cleated belt conveyors can integrate with other automation systems for material presentation, increasing efficiency. The diversity of cleat configurations makes them appropriate for products with irregular shapes or inconsistent sizes.
Recycling Facilities
Cleated conveyors have important applications in the recycling industry, moving sorted materials as glass, metals, and plastics. The strong cleats are specially designed to handle awkwardly shaped materials and prevent them from slipping back. Cleated belt conveyors are designed with heavy-duty materials that can stand up to the corrosive nature of many recycling fields, including garbage and rubbish.
Cleat Type and Height
Choosing the right cleat type and height for a conveyor, cleated belt, and conveyor system largely depends on the material that has to be moved and the inclination angle of the conveyor. Rubber conveyor belts with side walls are ideal for agitating materials because they are thick and can handle them without falling over. Chevron or v-shaped cleats would be best for boosting unitop stability because they offer better grip and find it easier to keep the load stable on an inclined surface. In the case of steep inclines or loose products like grains or powders, the height of the cleat must be considered. Higher cleats give better stability, but they might require more space and might not be suitable for certain applications. For items that are heavy or have irregular shapes, the use of herringbone belts with side walls should also be considered, as they would provide additional friction and thus prevent the object from toppling over during the transportation process.
Industry Requirements
Cleated conveyor belts can be an invaluable asset in several industries. They are critical in the food production industry, where hygiene and sanitation are paramount. Conveyor belts in the food industry should be designed for easy cleaning with non-porous materials for surfaces that will be in contact with the food. The mining and recycling industries put tremendous stress on their equipment. Selecting a heavy-duty, wire-reinforced cleated belt with abrasion and corrosion-resistant features is important here. In manufacturing and warehousing, flexibility and importance are key.
If faced with such an issue, it is advisable to choose a cleated belt conveyor suitable for the load to be conveyed and the distance to be covered. Consideration must also be given to the ambient conditions the system will work. There are cleated belts designed for high temperature, high humidity, and even highly corrosive chemical environments.
Belt Material
Several material options for the cleated belt conveyor are available, depending on the operation conditions and the field material. Rubber-clad belts provide good friction and are perfect for wet and dry fields. PVC belts are easily cleanable and can be used in various fields, including food processing. Also, wire-reinforced belts offer higher toughness and are suitable for handling big or sharp field materials. Choosing the right material for the belt itself will considerably influence its longevity and performance.
Belt Maintenance and Durability
Longevity and performance are vital considerations when selecting a cleated belt conveyor. A low-maintenance conveyor is preferable in most working environments. Rubber belts can be relatively easy to take care of, but they can also wear out sometimes, especially in rough working conditions. Regular inspection for wear and tear, proper lubrication on the belt system, and prompt repairs/snap-tights are some of the maintenance activities that can enhance the cleated belt conveyor's longevity. Besides, a belt designed with increased resistance to wear, tearing, and environmental conditions will require minimal intervention as it provides a longer service life concerning the field conditions.
A1: The sort of cleated belt conveyor depends on the prime material and the angle of the incline. Horizontal, inclined, or abrupt transitions are tricky, while horizontal belts are most suited for gradual inclines.
A2: Cleated belt conveyors are widely used in logistics and manufacturing for organizing and staging parts, in warehouses for transporting bulk goods, and in assembly lines for moving products as per the manufacturing process needs.
A3: Cleated belts are ideal for conveying irregularly shaped items as they are expertly designed with raised sections that hold the item in place, preventing it from tipping or sliding off while moving through the conveyor system.
A4: Cleated belt conveyors are easily changeable through cleat design, spacing height, and belt material. Users can customize the pace, gap, and shape of the cleats and the belt composition to perform well in the specific applications that users intend to use the conveyors for.
A5: Any special maintenance practices should be implemented, such as frequent cleaning, inspection for wear and tear, and proper alignment and tensioning of the belts. This can help extend the life of the systems further and ensure they work as productively as possible.