
All categories
Featured selections
Trade Assurance
Buyer Central
Help Center
Get the app
Become a supplier

(916 products available)



































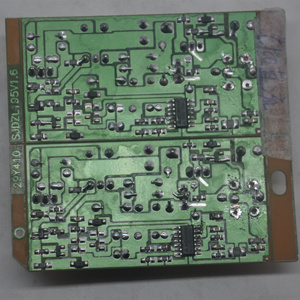
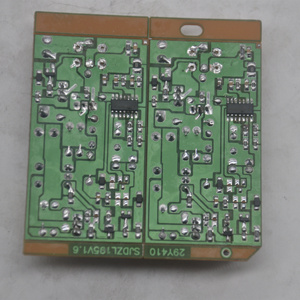

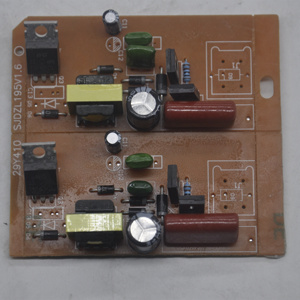







A CDI circuit is an electronic circuit used to control the ignition timing of an internal combustion engine. It ensures optimal engine performance, fuel efficiency, and emissions control. There are several types of CDI circuits, each designed to meet specific engine requirements and performance levels.
Capacitor Discharge Ignition (CDI) Circuit
This is the most common type of CDI circuit used in motorcycles and small engines. It stores energy in a capacitor and discharges it through the ignition coil at regular intervals. This results in a strong, consistent spark that improves engine performance and reliability.
Transformer-based CDI circuit
This type of CDI circuit uses a transformer to boost the voltage generated by the capacitor discharge. This results in an even more powerful spark, making it suitable for high-performance engines or racing applications.
Inductive Ignition System
This is a traditional ignition system still used in many older vehicles and some small engines. It uses a battery, ignition coil, and points-based distributor to generate a spark. While simple and reliable, inductive ignition systems are less efficient and have weaker sparks compared to CDI circuits.
Digital CDI circuit
Digital CDI circuits are used in modern motorcycles and some high-performance engines. They use digital microcontrollers to control ignition timing based on various engine parameters such as RPM, throttle position, and temperature. This allows for more precise ignition control, resulting in better performance, fuel efficiency, and lower emissions.
Variable Timing CDI (VTCDI)
VTCDI is commonly used in performance tuning kits for motorcycles and ATVs. It allows users to adjust and optimize ignition timing for specific fuel types, engine modifications, and performance goals. VTCDI enables better tuning flexibility, resulting in increased power and torque for customized applications.
Programmable CDI
Programmable CDI circuits are advanced ignition control systems used in high-performance racing engines and aftermarket performance upgrades. These CDI circuits can be programmed to control ignition timing, ramp, and other parameters according to specific performance requirements. This allows for precise tuning, maximizing engine performance, and optimizing fuel efficiency.
The following are specifications for the different components of the CDI circuit:
Capacitor:
The capacitor in a CDI circuit is a key component that stores energy until needed. It has a capacitance value ranging from 0.5 to 10 microfarads in the CDI ignition system. The capacitor charges quickly through a resistor from the battery or generator's output voltage. It also discharges rapidly, delivering a high-current pulse to the ignition coil when the switch opens. This property allows the capacitor to provide a powerful spark for reliable combustion of the air-fuel mixture and a quick response to throttle changes.
Coil:
The CDI circuit coil generates a high-voltage pulse for ignition. It has two main windings: the primary and secondary. The primary winding receives a current pulse from the CDI circuit, while the secondary winding delivers a high-voltage pulse to the spark plug. The CDI coil is cylindrical and has a core made of iron or ferrite. It also has many turns of wire in the primary and secondary windings, which generate a magnetic field when current flows through them. The coil also has a capacitor connected across the primary winding. This capacitor helps smooth out the current pulse and improves spark quality.
Transistor:
The transistor in a CDI circuit functions as a switch that controls the current flow in the primary winding of the ignition coil. It receives signals from the timing circuit and opens or closes the circuit. When the transistor receives a signal from the timing circuit, it connects the current flow from the battery or generator to the primary winding of the ignition coil. This action generates a magnetic field in the coil, and the secondary winding produces a high-voltage pulse. The CDI circuit transistor is usually a power bipolar junction transistor (BJT) or field-effect transistor (FET) with high current and voltage ratings.
Timing circuit:
The timing circuit in a CDI circuit controls when the transistor switches on and off. This function determines the timing of the ignition spark in relation to the position of the engine's pistons. The timing circuit receives signals from the engine's speed and load sensors. It also processes these signals and generates a timing signal for the ignition coil's primary winding. The timing circuit can be an analog circuit with resistors, capacitors, and other discrete components. It can also be a digital circuit with a microcontroller or programmable logic device.
Regular maintenance is essential to ensure the CDI functions properly. Below are some of the maintenance requirements:
Choosing the right Capacitor Discharge Ignition (CDI) circuit for specific needs requires careful consideration of several key factors:
Check the User Manual
Read the user manual to know the cdi circuit's location and the bike's safety instructions.
Gather Tools and Safety Gears
Wear safety gears like gloves and goggles. Get the needed tools, like screwdrivers, wrenches, and a torque wrench.
Find the Right Replacement
Ensure that the replacement matches the old one. Compare the new cdi circuit diagram to the old one. Check that the plugs, shape, and numbers match.
Disconnect the Battery
Avoid short circuits or shocks by disconnecting the battery before changing the CDI.
Remove the Old CDI
Use a screwdriver or wrench to take out the bolts holding the cdi circuit. Carefully remove it without damaging the wires or other parts. Take care not to strip the screws or damage the surrounding components.
Connect the New CDI
Put the new cdi circuits in the same way as the old one. Do not pull the wires. Ensure that the plugs and other parts match perfectly.
Check the Manual for Special Steps
If there are any special steps for fixing a cdi circuit in that bike, follow them now. Reconnect the battery and check all connections.
Test the Bike
Start the bike to see if it runs well. Test the speed and other parts to ensure everything is perfect.
Put Everything Back
When satisfied, put the covers and anything else removed back in place. Keep the tools in a safe place.
Q: How do I know if my CDI circuit is working?
A: There are a few signs to look for that can tell if the CDI is faulty. The first sign is if the engine doesn’t start or has a hard time starting. Another sign is if the engine has a rough idle or if it misfires. The last sign is if the engine loses power or hesitates when accelerating. If these signs are present, the CDI circuit may be faulty.
Q: Can I upgrade my CDI?
A: Yes, it is possible to upgrade the CDI. An upgraded CDI can improve engine performance, especially in vehicles with modified engines. The upgraded CDI helps the engine run smoothly and efficiently.
Q: What is the maintenance required for CDI?
A: There is no special maintenance required for the CDI. However, keeping it in good condition is important. Avoid exposing it to extreme conditions such as high heat or moisture. Regular maintenance of the engine makes sure that the CDI works well.
Q: Can a faulty CDI be repaired?
A: In most cases, a faulty CDI cannot be repaired. CDI units are complex electronic devices, and damage to the internal components is usually irreversible. It is generally more reliable and cost-effective to replace a faulty CDI with a new one.
Q: Does a higher-priced CDI mean better performance?
A: Not always. While a higher-priced CDI may offer additional features or be of better quality, it does not necessarily mean better performance. The performance of a CDI depends on its compatibility with the engine and its ability to provide a consistent and accurate ignition timing.