
All categories
Featured selections
Trade Assurance
Buyer Central
Help Center
Get the app
Become a supplier

(6225 products available)


































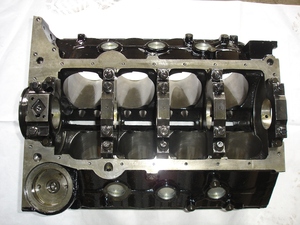










An casting engine cylinder block is an integral part of a vehicle's engine. It is often referred to as the engine block. Vehicle engines have one or more cylinders that create a space where fuel and air mix and combust to generate power that moves the vehicle.
The engine cylinder block is the foundation of the entire engine and holds the cylinders, which are essential for the engine's functioning. It also houses other important components like the crankshaft, camshaft, and oil passages. Essentially, anything related to engine management is likely to be found on the engine cylinder block.
The casting engine cylinder block is critical for maintaining the alignment and support of these components. It needs to be durable and resistant to the extreme forces and heat generated by the engine. Because of its importance, people should understand its types to know how to maintain it better and learn its features.
V-type engine cylinder blocks:
The V-type casting engine cylinder blocks have a V-like shape that accommodates two rows of cylinders angled concerning each other. Each row has one or more cylinders that create a V shape. The engine's crankshaft is located at the bottom of the V. V-type engines are renowned for their smooth operation and compact size, making them suitable for vehicles that require a small and powerful engine.
Inline engine cylinder block:
These casting engine cylinder blocks are the most straightforward in design and construction. As the name suggests, the cylinders are arranged in a single line or row. Inline engine blocks are easy to manufacture and are usually cheaper than the V-type and flat engines. They also have a simple design that makes maintenance easy. For example, all the cylinders can be accessed easily without removing anything. Because of these advantages, inline engine blocks are popular in small vehicles and budget-friendly cars.
Flat engine cylinder blocks:
A flat engine block is similar to the V-type engine block, but it has an even more compact design. The cylinders in a flat engine block are horizontal and placed in two rows parallel to each other and to the crankshaft. This engine block design is suitable for sports cars, which need a powerful engine that can run smoothly without taking too much space.
The specifications of large engine blocks can be bewildering to the layperson. For example, consider a V6 truck engine block specification.
Maintaining the engine cylinder block is critical to ensuring that it lasts long and works effectively. Here are general tips on maintaining engine blocks:
Before buying a vehicle, business buyers must consider the cylinder block size and type to ensure it matches their needs and preferences.
Compatibility
Ensure the casting engine cylinder block is compatible with the existing components of the target vehicle or machinery. This includes the compatibility with the cylinder head, crankshaft, and other key parts to avoid future disruptions and conflicts.
Size and weight
For heavy and large vehicles, larger and bigger blocks may be required for additional engine power. However, casting engine cylinder blocks that are too large and heavy may be inconvenient for smaller and compact vehicles. Consider the size and weight of the engine cylinder block to ensure it matches the vehicle size.
Budget
Generally, larger and bigger casting engine blocks tend to be more expensive. Meanwhile, smaller blocks may require additional costs for frequent maintenance and repairs. Thus, consider the long-term costs and the initial investment when choosing a casting engine cylinder block.
Future upgrades
If there is a plan to upgrade the vehicle to enhance its performance in the future, choose a casting engine cylinder block that will allow future modifications and upgrades. This can be beneficial for the business in the long run.
Replacing a casting engine block is a complicated process that requires a lot of technical knowledge, accuracy, and specialized tools like torque wrenches. Below is a step-by-step guide on how to replace an engine block:
Q1: What is a cylinder block?
A1: The cylinder block is the engine's main part. It acts as the basis for the other parts and has holes called cylinders where the pistons move up and down. The cylinder block also holds the coolant to help keep the engine from overheating.
Q2: What are the types of casting engine cylinder blocks?
A2: There are two types of casting engine cylinder blocks: the cast iron engine cylinder block and the aluminum engine cylinder block. The former is popular because of its durability. The latter is lighter and has better corrosion resistance.
Q3: Is it possible to upgrade a car's engine using a larger engine casting cylinder block?
A3: Yes, a larger engine casting cylinder block can be used to upgrade an existing engine. However, this might require other modifications, such as changing the exhaust system, intake system, and cooling system, to accommodate the new cylinder block.
Q4: What are the advantages of a larger engine casting cylinder block?
A4: A larger engine casting cylinder block creates more power by generating more torque. It has a longer stroke length, allowing more air and fuel to enter the cylinders and producing more energy.