(31144 products available)





































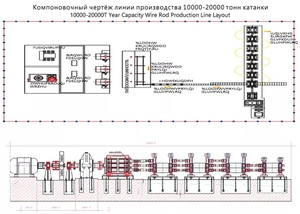






















































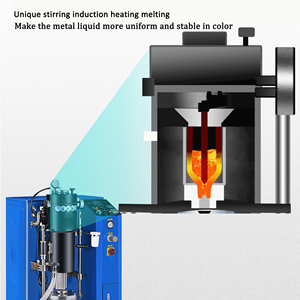

























































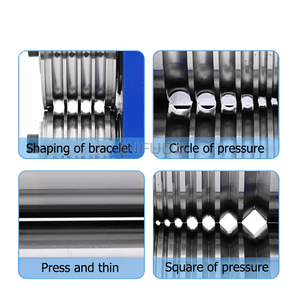






























A casting and rolling machine is an integrated equipment for metal casting and rolling processes. Different types of machines are used according to the scale of production and specific needs.
Continuous Casting Rolls:
These machines are commonly used for producing non-ferrous metals, such as copper and aluminum. They employ a cooled rotating cylinder assembly to create thin metal strips or slabs. The cooling cylinder assembly typically consists of water-cooled cylinders with consumable casting rolls. The molten metal is poured over the rotating cylinder, and as it cools down, a solidified strip is formed and rolled up. Continuous casting rolls feature a water spray cooling system, anti-tarnish devices, various control systems, and automatic roll changing functions.
Horizontal Casting and Rolling Machines:
Such machines are commonly used in metallurgy to vertically cast molten metal into a familiar shape, such as a slab or ingot. The setup consists of a casting Unit with a mold assembly, a solidification unit with a cooling chamber, and a rolling mill to shape the casted metal to desired dimensions. Sometimes, the machines also feature a separating unit and an automatic handling system.
Combined Casting and Rolling Machines:
Often referred to as CR mills, these combined casting and rolling machines are designed to simultaneously cast and roll materials like steel, aluminum, or any other metal alloys in a single setup. The integration of the two processes within one machine offers several advantages, such as eliminating the need for intermediate reheating and reducing processing time and production costs.
Capacity:
The ability of a casting and rolling machine is represented by the quantity and weight of slabs, which varies according to the size of the machine. Typically, small models can produce casting-rolling slabs.
Productivity:
Productivity indicates the number of slabs produced by the machine in a specific period, usually represented by hourly output or daily output. Casting and rolling machines of different models and sizes may show different productivity rates, usually between several to dozens of slabs per hour or from a dozen to a hundred per day.
Operation mode:
Machines for casting and rolling are generally divided into continuous and periodic operation modes. The continuous mode allows for uninterrupted production of casting-rolling slabs, whereas the periodic mode involves repeated processing of the same number of casting and rolling slabs in batches.
Material compatibility:
Alloy steel casting and rolling machines and non-alloy steel machines differ in structure, technical parameters, and operational processes. As a result, the variety and specification of the casting and rolling steel that the machines produce are also different.
Automation level:
The degree of automation encompasses everything from simple manual operations to more sophisticated semi-automatic and full-automatic control systems. In fully automated machines, for example, the entire production process from feeding to discharging can be managed and controlled by an electronic system, thus enhancing efficiency and accuracy.
Driving Method:
It can be electric, hydraulic, or pneumatic. For example, the driving method for hydraulic casting and rolling machines involves using hydraulic systems to provide power, offering advantages such as high torque, good operating performance, and suitability for handling heavy loads.
Weekly Maintenance:
Weekly maintenance includes checking and adding lubricating oil to each part, checking for any loose bolts or screws, tightening them if found loose, checking for damaged or worn parts, and replacing them if necessary, and cleaning the casting table and furnace to keep it free from debris and impurities.
Monthly Maintenance:
The monthly maintenance of the casting and rolling machine consists of examining the electric control system, inspecting the hydraulic system, balancing the roll gap, and adjusting the roll gap according to the slab thickness to ensure the uniformity and accuracy of the slab thickness.
Long-term maintenance:
Cleaning components like hydraulic components, transmission components, and electrical components is part of the periodic maintenance of the casting and rolling machine. The procedure calls for dust cleaning and the wiping away of any dirt or oil. Additionally, each component's operating status must be checked to ensure there are no leaks in the hydraulic system, perfect gear engagement in the transmission system, and reliable function of the electrical system.
The areas of application of die casting and rolling machines are as vast as the industries that use metals. The advantage of these machines being able to shape several types of metals makes them suitable for use in the following industries.
Cobalt Chromium Alloys
Determining the machine's capacity to process specific alloys, such as cobalt chromium alloy for dental and other applications, is crucial. These alloys require precise casting and rolling capabilities to produce high-quality, consistent materials. The chosen machine should be compatible with these specific alloy materials to ensure proper functioning and optimal results.
Productivity
When selecting a casting and rolling machine, it's important to consider its productivity. This refers to the amount of alloy it can process within a given timeframe. Machines with higher productivity rates can help businesses meet demand more efficiently by producing more material in less time.
Efficiency
Efficiency is another crucial factor to consider when choosing a casting and rolling machine. An efficient machine will not only produce more material but also use resources, such as energy and alloy, more effectively. This can result in cost savings and increased output for a business.
Cost
The price of the device is clearly a significant factor in the selection process. However, it should be noted that different models may differ in price due to various features and capabilities. While some machines might come at a higher cost, they may offer more advanced features or be better suited for specific business needs.
Technological Updates
Technological advancements in casting and rolling machines have led to improvements in accuracy, efficiency, and ease of use. It's essential for businesses to stay updated on the latest technologies to ensure they are investing in a machine that will provide the best performance and support their production needs.
Safety Regulations
Safety is a paramount concern when it comes to choosing any industrial machinery, including casting and rolling machines. These devices must adhere to specific safety standards and regulations to protect workers and prevent accidents. By choosing a machine that complies with these safety regulations, businesses can help ensure the safety of their employees and reduce the risk of potential accidents.
Q1: How can investors ensure the quality of the molten metal during the casting process in a casting and rolling machine?
A1: By investing in effective metal purification systems like degassing units, filtration apparatus, and electromagnetic stirrers, alloy selection and stringent environmental controls during the melting and casting phases are also crucial.
Q2: What are the trends in casting and rolling technology that investors should watch?
A2: Pay attention to the emergence of energy-efficient machines, automation and AI integration, precision casting and rolling innovations, and flexible modular systems.
Q3: What type of maintenance should be performed on a casting and rolling machine?
A3: Regular inspections, lubrication, part replacements, calibration, software updates for automated systems, cleaning to prevent material build-up, and corrosion control are essential.
Q4: How can the energy consumption of a casting and rolling machine be optimized?
A4: Use energy-efficient models, recover waste heat for other processes, maintain optimal machine operating temperatures, and implement energy management systems to monitor and regulate energy use.
Q5: Are there safety features that should be integrated into a casting and rolling machine?
A5: Yes, look for safety elements like emergency shutdown buttons, guards to prevent accidental contact with moving parts, overload protection, and safety interlocks. Operators' training on safety practices is also vital.