(1256 products available)







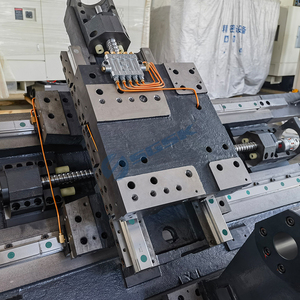




























































































































































































An automatic lathe machine makes pieces of any shape from any type of solid material by turning, usually cylindrical. The basic parts that are common to all automatic lathes are the workhead, which holds the workpiece as it turns; the toolhead holds the cutting tools; and the feed mechanism, which advances the workpiece or cutting tools.
The two main types of lathe machines are:
Conventional Lathes:
A conventional lathe operation runs on electricity. The various parts that make up a lathe machine can be studied with the help of a diagram. Generally, a lathe machine is rectangular, and at one end, there is an electric motor that helps to turn the workpiece. On the top side, there are various cutting tools. A work carriage helps to move the workpiece.
The motor drives a belt after which the spindle is made to rotate. The driving system helps to move the workhead, feeding mechanism, and tool post. The tool post holds the cutting tools, which could vary depending on the type of work that needs to be done. Some examples of cutting tools are drill bits, thread cutting, and groove cutting taps. A tool holder is used to hold the cutting tools firmly, and the tailstock helps to support the workpiece. In this type of lathe, the tool post and cutting tools have to be changed manually.
Transformers:
An automatic transformer lathe has a digital control unit that monitors the work that is done on the metal piece. The digital control unit helps to regulate the speed at which the work piece turns. It can also set the various cutting actions that need to be carried out. Unlike a conventional automatic lathe, the tool post in a transformer lathe is automatically changed to the required tools. An electronic device will determine the speed and direction of the metal workpieces. The main difference between a transformer and a conventional lathe machine is that the motor, feeding mechanism, and tool post are all automatically controlled by an electronic device. A transformer lathe machine can perform its work faster and more accurately than a conventional lathe machine. The digital control unit allows the operator to change the cutting tools as needed quickly. Unlike a conventional lathe machine, where only the tailstock is used to support the work piece, in a transformer lathe, there is a work holding device with a fixed jaw, moving jaw, and rear jaw.
Specifications of CNC automatic lathe producers may vary but here are some standard specifications with details.
Spindle Diameter
The spindle diameter is the length of the part that the automatic lathe machine can hold, usually measured in inches. The spindle diameter can determine the size of the materials or parts that can be processed or machined using the lathe machine. Larger spindle diameters allow for the machining of larger workpieces, while smaller spindle diameters are suitable for smaller workpieces.
Spindle Speed
The spindle speed refers to how fast or the rate at which the spindle of the automatic lathe machine rotates. The spindle speed is measured in revolutions per minute (RPM). Spindle speeds may vary depending on the material being machined. Higher spindle speeds enable faster machining of materials and workpieces.
Feed Rate
The feed rate in an automatic lathe machine refers to the distance that the cutting tool moves or advances during each rotation of the spindle. The feed rate is usually measured in inches per revolution. The feed rate determines the depth and rate at which the material is cut. It may also affect the surface finish and accuracy of the machined part.
Number of Axes
An automatic lathe machine may have multiple axes, allowing for more complex machining operations. An axis in a lathe machine refers to a straight line or pivot point around which the workpiece rotates. Traditionally, an automatic lathe machine has only two main axes, which are used for straight cuts and cylindrical shaping. More advanced lathe machines may have additional axes for greater machining flexibility.
Cutting Tools
A cutting tool is any tool that is used to cut and shape materials, including metals, plastics, wood, and ceramic, among others. In an automatic lathe machine, specialized cutting tools are used to perform various machining tasks, such as turning, threading, facing, grooving, and knurling.
For an automatic lathe CNC machine to work effectively for long periods, it is important to maintain it effectively. Here are some maintenance tips to keep the machine in perfect condition:
Regular Cleaning
An automatic lathe machine should be regularly cleaned to remove debris, dust, and coolant residue. A vacuum or blow gun can be used to get rid of any leftover chips from the workpiece or tooling in hard-to-reach spaces.
Inspection of Tools and Parts
Cutting tools, belts, and blades should be routinely inspected for sign or casing of damage such as wearing or nicks. Any damaged part should be replaced and repaired to preserve automatic lathe machine precision and functionality.
Lubrication
Maintain proper functioning and performance of the automatic lathe machine by regularly lubricating all moving parts. Lubrication helps reduce friction between parts, wear and tear, and overheating.
Calibration
Regular calibration of the lathe machine ensures that it maintains accuracy and precision with its cutting and machining operations. Machine settings may need to be adjusted to compensate for tool wear and environmental changes.
Dust and Chip Extraction
An automatic CNC lathe machine is equipped with dust extraction systems that operate during machining. The extraction systems eliminate dust and chips from the machining area to ensure a clean working environment and minimize the risk of damage to the machine.
Industrial machinery and parts:
A wide range of complex pieces, such as machine shafts, spindles, couplings, valve bodies, gear shafts, and other mechanical parts requiring precise machining and complex forms, can be created with the help of CNC (computer numerical control) lathes. CNC lathes are capable of mass-producing these mechanical components while maintaining their dimensional accuracy and conformity.
Automotive and motorcycle components:
An essential component of the automotive industry, automatic lathes also include motorcycle components. Automatic lathes can precisely manufacture various types of vehicle parts, such as wheel hubs, axles, and cylinder valves.
Home appliances and accessories:
Automatic lathes can also produce components and accessories for different types of home appliances, such as refrigerator valves, washing machine shafts, juicer blades, and mixers. These pieces typically require a higher lathe tolerance and smoother surfaces to ensure the quality and performance of home appliances.
Cellphones and 3C digital accessories:
Automatic lathes are also used to make precise and delicate 3C digital accessories, including mobile phone parts like camera frames, SIM card slots, and other electronic components.
Furniture hardware and fittings:
Hinges, handles, locks, and other furniture hardware fittings can be manufactured precisely and quickly with the help of automatic lathes, enabling the furniture's smooth functioning and stability.
Medical equipment and parts:
The essential precision components of medical equipment are often made with the help of automatic lathes, including endoscope components, surgical instruments, orthopedic implants, and more complex and precise medical equipment.
Aerospace components and accessories:
CNC lathes can make precision parts like brackets, connectors, and turbine blades for aerospace industries, among others, which are utilized in aircraft, satellites, and space vehicles.
Choosing an automatic lathe producer involves several key factors. First, buyers need to evaluate the projects that the lathe will handle. The project's complexity, the materials to be used, the required precision and tolerances, and the production volume will influence the type of lathe suitable for the job. For example, for high-volume production of small, complex parts, a CNC automatic lathe with a large spindle capacity may be the best choice.
Second, buyers should consider the level of automation needed. Some lathes offer basic automated functions, such as automatic tool change, while others provide full automation with bar feeding, part fetching, and CNC control. Choosing a lathe with the right level of automation can enhance productivity and reduce labor.
Third, the machine's physical size is an important consideration. Will the lathe fit into the shop floor space? Also, what are the weight and dimensions of the parts being produced. Buyers don't want a machine that will cramp their production space or be unable to move it.
The machine's operating system and controls are important things to consider. Does the machine support remote monitoring and diagnostics? Does it have advanced features like tool path simulation and virtual workspaces? The answers to these questions will determine the productivity and ease of maintenance of the entire production system.
Finally, buyers must consider the producer's reputation and service capabilities. They should choose a producer known for high-quality machines and good after-sales service. The producer should provide installation, training, and timely spare parts supply to ensure the lathe's smooth operation and longevity.
Q1: Do all automatic lathes work the same way?
A1: No, all automatic lathes do not work the same way. Different types of lathe machines have varying mechanisms for handling and machining workpieces.
Q2: Can an automatic lathe produce threads?
A2: Yes, an automatic lathe can produce threads. However, the threading method depends on the type of automatic lathe in use. For instance, an eccentric thread cutting gear can be used to cut threads on an automatic screw-cutting lathe.
Q3: How fast can an automatic lathe producer work?
A3: The speed of an automatic lathe producer depends on several factors, including the type of lathe, its design, the material being machined, and the operation being performed. Generally, an automatic lathe can achieve speeds of between 2000 and 6000 RPM.
Q4: Can an automatic lathe produce threads?
A4: Yes, an automatic lathe can produce threads. However, the threading method depends on the type of automatic lathe in use. For instance, an eccentric thread cutting gear can be used to cut threads on an automatic screw-cutting lathe.