
All categories
Featured selections
Trade Assurance
Buyer Central
Help Center
Get the app
Become a supplier

(9563 products available)











































An AC DC welder is a machine that joins metal workpieces. These welders may use alternating current (AC), direct current (DC), or both to weld. They come in various types:
An AC stick welder uses only AC current. It is a simple and inexpensive welding machine. The machine uses a consumable electrode covered in flux. The flux coating protects the weld pool from contamination. It also releases gas to shield the weld pool from atmospheric gases. AC stick welders can weld dirty or rusty metals, but the welds aren't very strong. They may also require frequent cleaning of the slag and re-striking the arc.
The DC stick welder is an upgrade of the AC stick welder. It uses direct current, which allows for better control and stronger welds. DC stick welders produce smoother and more stable arcs than AC machines. They are also less likely to cause weld defects. However, DC stick welders are more expensive than AC stick welders.
An AC/DC stick welder can weld with both AC and DC currents. It is more versatile than the AC and DC stick welders. The AC/DC machine can be used for various welding applications. It is also more expensive than single AC or DC welders. However, the AC/DC stick welder isn't as powerful as multi-process welders.
Like the stick welder, the AC/DC TIG welder can use either AC or DC. It is more versatile than the regular TIG welder, which uses only DC. The AC mode is suitable for aluminum and magnesium. The DC mode is ideal for stainless steel, copper, and other non-ferrous metals. The AC/DC welder is more expensive than the single-process TIG welder.
The MIG welder uses a continuously fed wire as an electrode. It also uses an inert gas to shield the weld pool. The MIG welder can use either AC or DC current. MIG welding is faster and easier than stick welding. It is also more suitable for welding thin workpieces. The welder can use different gas mixtures and types of wires for various applications.
AC DC TIG welders have numerous specifications. Here are some of them.
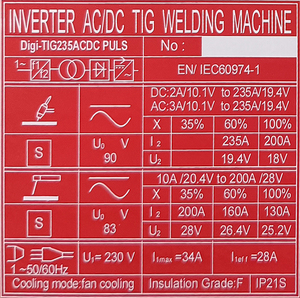
Input power is measured in voltage and amperage. It shows the welding machine's power requirements. Most AC DC welders use 110/115/120 V. They also use 220/230/240 V. The 110 V welders are suitable for light-duty work. The 220 V ones are ideal for heavy-duty welding tasks.
AC DC welders produce a certain amount of current and voltage for welding. This is known as the output current and voltage. The output current is measured in amperes (A), while the output voltage is measured in volts (V). The output current and voltage determine the type of materials the AC DC welder can weld. If it is high, it can weld thick metals.
The duty cycle is the amount of time the AC DC welder can be used in a 10-minute period. Manufacturers usually express it as a percentage. They often write it like this: 60% at 110A. This means the welder can work for 6 minutes at a setting of 110A. After that, it rests for 4 minutes.
The size and weight of the AC DC welder varies. It depends on the welding process, amperage, and features of the welder. Some models are portable, while others are stationary.
Proper maintenance of an AC/DC welder can help it last for a long time. Welders must carry out the following maintenance tips:
AC DC welders have a wide range of applications in various industries. Here are some common application scenarios for these welders.
In industries such as construction, automotive, and manufacturing, AC DC welders are used to join and repair metal components. They can weld materials like steel, aluminum, and stainless steel to create structures, frames, and parts, among others.
AC DC welders can be used to repair and maintain machinery and equipment in industries like agriculture, mining, and energy. They weld damaged parts or perform routine maintenance to keep the equipment in good working condition.
In the oil, gas, and water industries, AC DC welders are used to weld pipes. They ensure the pipelines are tightly connected, preventing leaks and ensuring the safe transportation of liquids.
AC DC welders are also used in construction to join metal frameworks, bridges, and buildings, among other structures. They create a strong foundation for infrastructure projects.
Professionals use AC DC welders to repair vehicles by welding metal parts such as frames, exhaust systems, and engine components. Welders provide cost-effective solutions for automotive repairs.
AC DC welders are used to make jewelry or repair damaged pieces in the jewelry-making industry. They precisely weld small metal components like gold, silver, and platinum without damaging delicate jewelry parts.
When choosing the right AC DC welder for a project, it is important to consider the following factors:
It is important to consider the type of metal being welded, as well as its thickness. Some types of metals are more compatible with certain welding processes. For example, TIG welding is typically used for welding thin sheets of stainless steel, while MIG welding is better for materials like aluminum. The thickness of the material also matters, as more power and heat control may be necessary for thicker metals.
Consider the welding process that will be used for the project, as well as the technique. Each welding process requires a specific type of welding machine that is compatible with it. For example, MIG welders use a wire electrode that is fed through a gun, while TIG welding uses a non-consumable tungsten electrode. Choose an AC/DC welder that is suitable for the desired welding process and technique.
Depending on the specific needs of the project, consider the portability of the welding machine. Some AC DC welders are designed to be lightweight and easy to transport, while others are larger and more stationary. For projects that require welding in multiple locations, a portable welder may be preferable. However, for heavy-duty welding tasks, a more stationary machine with higher power may be necessary.
When choosing an AC DC welding machine, it is important to consider the power source and output. Welders can use various power sources, including alternating current (AC), direct current (DC), or both (AC/DC). Each power source has its own strengths and weaknesses. For example, AC power is typically used for welding magnetic metals, while DC power creates a more stable arc. Additionally, it is necessary to consider the machine's power output, as different welding tasks may require varying levels of power.
Q1: What is the difference between an AC welder and a DC welder?
A1: The main difference between an AC and a DC welder is the type of current they use. The two welders also work differently. An AC welder changes its direction of current flow after a certain period, while a DC welder has a constant flow of current in one direction.
Q2: Can an AC welder weld aluminum?
A2: Yes, it can. However, using an AC welder to join aluminum is more challenging than using a DC welder. This is because the oxide layer on the aluminum interferes with the welding process. Therefore, welders must use a special technique known as the high-frequency start to join aluminum with an AC welder.
Q3: Can someone weld with AC instead of DC?
A3: No. AC and DC current are not interchangeable. Welding with the wrong current can lead to porous welds, entrapment of slag, and lack of penetration, among other issues.